The inodilator levosimendan in repetitive doses in the treatment of advanced heart failure
- PMID: 29249905
- PMCID: PMC5932565
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/sux004
The inodilator levosimendan in repetitive doses in the treatment of advanced heart failure
Abstract
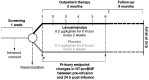
Inotropes may be an appropriate response for some patients with advanced heart failure who remain highly symptomatic despite optimization of evidence-based therapy. These patients need to be supported waiting for a heart transplant or ventricular assist device, or may be candidates for inotropy as an intervention in its own right to maintain a patient in the best achievable circumstances. Objectives in such a situation include relieving symptoms, improving quality of life and reducing unplanned hospitalizations and the costs associated with such admissions. Levosimendan, a calcium sensitizer and potassium channel opener with inotrope and vasodilator actions, has emerged as a potentially valuable addition to the armamentarium in this context, used in repeated or intermittent cycles of therapy. Detailed proposals and guidance are offered for the identification of candidate patients with good prospects of a beneficial response to levosimendan, and for the safe and effective implementation of a course of therapy.
Keywords: Advanced heart failure; Intermittent; Levosimendan; Rehospitalization; Repetitive.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repetitive levosimendan treatment in the management of advanced heart failure.Eur Heart J Suppl. 2018 Dec;20(Suppl I):I11-I20. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/suy040. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2018. PMID: 30555280 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive use of levosimendan in advanced heart failure: need for stronger evidence in a field in dire need of a useful therapy.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Sep 15;243:389-395. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.05.081. Epub 2017 May 23. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28571618 Review.
-
Repetitive use of levosimendan for treatment of chronic advanced heart failure: clinical evidence, practical considerations, and perspectives: an expert panel consensus.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Jun 15;174(2):360-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.04.111. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24780540
-
Planned repetitive use of levosimendan for heart failure in cardiology and internal medicine in Sweden.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Jul 15;175(1):55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.04.243. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24820737
-
The potential of the inodilator levosimendan in maintaining quality of life in advanced heart failure.Eur Heart J Suppl. 2017 Mar;19(Suppl C):C15-C21. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/sux003. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2017. PMID: 29249906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Levosimendan in the light of the results of the recent randomized controlled trials: an expert opinion paper.Crit Care. 2019 Nov 29;23(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2674-4. Crit Care. 2019. PMID: 31783891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levosimendan Efficacy and Safety: 20 Years of SIMDAX in Clinical Use.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;76(1):4-22. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000859. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32639325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levosimendan Efficacy and Safety: 20 years of SIMDAX in Clinical Use.Card Fail Rev. 2020 Jul 8;6:e19. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2020.03. eCollection 2020 Mar. Card Fail Rev. 2020. PMID: 32714567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Metra M, Ponikowski P, Dickstein K, McMurray JJ, Gavazzi A, Bergh CH, Fraser AG, Jaarsma T, Pitsis A, Mohacsi P, Böhm M, Anker S, Dargie H, Brutsaert D, Komajda M.. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Advanced chronic heart failure: a position statement from the Study Group on Advanced Heart Failure of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2007;9:684–694. - PubMed
-
- Desai AS. The three-phase terrain of heart failure readmissions. Circ Heart Fail 2012;5:398–400. - PubMed
-
- Desai AS, Stevenson LW.. Rehospitalization for heart failure: predict or prevent? Circulation 2012;126:501–506. - PubMed
-
- Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, Gallagher ER, Admane S, Jackson VA, Dahlin CM, Blinderman CD, Jacobsen J, Pirl WF, Billings JA, Lynch TJ.. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;363:733–742. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
