One-third of an Archivial Series of Papillary Thyroid Cancer (Years 2007-2015) Has Coexistent Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis, Which Is Associated with a More Favorable Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging
- PMID: 29250033
- PMCID: PMC5716977
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00337
One-third of an Archivial Series of Papillary Thyroid Cancer (Years 2007-2015) Has Coexistent Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis, Which Is Associated with a More Favorable Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging
Abstract
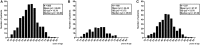
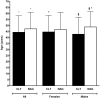
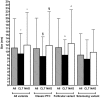
The significance and impact of the coexistence of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (CLT) with thyroid cancer is still debated. To verify the influence of CLT on papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), we retrospectively collected 505 PTC cases and analyzed age at diagnosis, sex, size, lymph node status, and staging. We found that CLT was present in 168 PTC (33.3%). Compared with the 337 patients without CLT (non-CLT), CLT patients were younger (44.42 ± 13.72 vs. 47.21 ± 13.76 years, P = 0.03), had smaller tumors (9.39 ± 6.10 vs. 12 ± 9.71 mm, P = 0.002), and lower rate of lymph node metastases (12.5 vs. 21.96%, P = 0.01, OR = 0.508). Tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging (T1a through T4) was more favorable for the CLT group compared to the non-CLT group (for instance, T1a = 65.5 vs. 49.8%, T3 = 4.8 vs. 23.4%). This study shows that one in three patients with PTC harbors CLT, which is associated with a more favorable TNM staging, consistently with a favorable outlook of PTC.
Keywords: autoimmune thyroiditis; autoimmunity; cancer; chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis; papillary thyroid cancer.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

