The Emerging Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium spartansii Isolated from Chinook Salmon: Comparative Genome Analysis and Molecular Manipulation
- PMID: 29250046
- PMCID: PMC5714932
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02339
The Emerging Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium spartansii Isolated from Chinook Salmon: Comparative Genome Analysis and Molecular Manipulation
Abstract
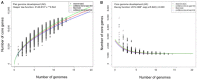
Flavobacterium spartansii strain T16T was isolated from a disease outbreak in hatchery-reared Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) fingerlings. To gain insight into its genomic content, structure and virulence pathogenesis factors, comparative genome analyses were performed using genomes from environmental and virulent Flavobacterium strains. F. spartansii shared low average nucleotide identity (ANI) to well-known fish-pathogenic flavobacteria (e.g., F. columnare, F. psychrophilum, and F. branchiophilum), indicating that it is a new and emerging fish pathogen. The genome in T16T had a length of 5,359,952 bp, a GC-content 35.7%, and 4,422 predicted protein-coding sequences. Flavobacterium core genome analysis showed that the number of shared genes decreased with the addition of input genomes and converged at 1182 genes. At least 8 genomic islands and 5 prophages were predicted in T16T. At least 133 virulence factors associated with virulence in pathogenic bacteria were highly conserved in F. spartansii T16T. Furthermore, genes linked to virulence in other bacterial species (e.g., those encoding for a type IX secretion system, collagenase and hemolysin) were found in the genome of F. spartansii T16T and were conserved in most of the analyzed pathogenic Flavobacterium. F. spartansii was resistant to ampicillin and penicillin, consistent with the presence of multiple genes encoding diverse lactamases and the penicillin-binding protein in the genome. To allow for future investigations into F. spartansii virulence in vivo, a transposon-based random mutagenesis strategy was attempted in F. spartansii T16T using pHimarEm1. Four putative gliding motility deficient mutants were obtained and the insertion sites of pHimarEm1 in the genome of these mutants were characterized. In total, study results clarify some of the mechanisms by which emerging flavobacterial fish pathogens may cause disease and also provide direly needed tools to investigate their pathogenesis.
Keywords: Flavobacterium spartansii; genome analysis; mutation; virulence factors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Flavobacterium spartansii sp. nov., a pathogen of fishes, and emended descriptions of Flavobacterium aquidurense and Flavobacterium araucananum.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014 Feb;64(Pt 2):406-412. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.051433-0. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24096350
-
Gamete-associated flavobacteria of the oviparous Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) in lakes Michigan and Huron, North America.J Microbiol. 2016 Jul;54(7):477-86. doi: 10.1007/s12275-016-5629-3. Epub 2016 Jun 28. J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27350613
-
Genomic diversity in flavobacterial pathogens of aquatic origin.Microb Pathog. 2020 May;142:104053. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104053. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32058022
-
Immunization with bacterial antigens: Flavobacterium and Flexibacter infections.Dev Biol Stand. 1997;90:179-88. Dev Biol Stand. 1997. PMID: 9270847 Review.
-
Emerging flavobacterial infections in fish: A review.J Adv Res. 2015 May;6(3):283-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2014.10.009. Epub 2014 Nov 7. J Adv Res. 2015. PMID: 26257926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Secretion Systems in Gram-Negative Bacterial Fish Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 15;12:782673. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.782673. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34975803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavobacterium erciyesense sp. nov., a putative non-pathogenic fish symbiont.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Nov;203(9):5783-5792. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02566-2. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34515811
-
Description of Flavobacterium cyclinae sp. nov. and Flavobacterium channae sp. nov., isolated from the intestines of Cyclina sinensis (Corb shell) and Channa argus (Northern snakehead).J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;60(9):890-898. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-2075-2. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35731344
-
Cooperative Interaction of Janthinobacterium sp. SLB01 and Flavobacterium sp. SLB02 in the Diseased Sponge Lubomirskia baicalensis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8128. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218128. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143227 Free PMC article.
-
A review of bacterial disease outbreaks in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) reported from 2010 to 2022.J Fish Dis. 2025 Sep;48(9):e13886. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13886. Epub 2023 Nov 15. J Fish Dis. 2025. PMID: 37965781 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

