Basic Properties And Clinical Applications Of The Intracardiac
- PMID: 29250250
- PMCID: PMC5673309
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.1444
Basic Properties And Clinical Applications Of The Intracardiac
Abstract
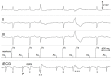
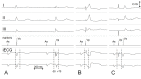
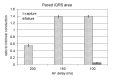
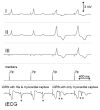
The electric signals detected by intracardiac electrodes provide information on the occurrence and timing of myocardial depolarization, but are not generally helpful to characterize the nature and origin of the sensed event. A novel recording technique referred to as intracardiac ECG (iECG) has overcome this limitation. The iECG is a multipolar signal, which combines the input from both atrial and ventricular electrodes of a dual-chamber pacing system in order to assess the global electric activity of the heart. The tracing resembles a surface ECG lead, featuring P, QRS and T waves. The time-course of the waveform representing ventricular depolarization (iQRS) does correspond to the time-course of the surface QRS with any ventricular activation modality. Morphological variants of the iQRS waveform are specifically associated with each activity pattern, which can therefore be diagnosed by evaluation of the iECG tracing. In the event of tachycardia, SVTs with narrow QRS can be distinguished from other arrhythmia forms based upon the preservation of the same iQRS waveform recorded in sinus rhythm. In ventricular capture surveillance, real pacing failure can be reliably discriminated from fusion beats by the analysis of the area delimited by the iQRS signal. Assessing the iQRS waveform correspondence with a reference template could be a way to check the effectiveness of biventricular pacing, and to discriminate myocardial capture alone from additional His bundle recruitment in para-Hisian stimulation. The iECG is not intended as an alternative to conventional intracavitary sensing, which remains the only tool suitable to drive the sensing function of a pacing device. Nevertheless, this new electric signal can add the benefits of morphological data processing, which might have important implications on the quality of the pacing therapy.
Keywords: CRT; Cardiac electrograms; Fusion detection; Hisian pacing.
Figures






References
-
- Irnich W. Intracardiac electrograms and sensing test signals: electrophysiological, physical, and technical considerations. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1985 Nov;8 (6):870–88. - PubMed
-
- Glikson Michael, Swerdlow Charles D, Gurevitz Osnat T, Daoud Emile, Shivkumar Kalyanam, Wilkoff Bruce, Shipman Tamara, Friedman Paul A. Optimal combination of discriminators for differentiating ventricular from supraventricular tachycardia by dual-chamber defibrillators. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005 Jul;16 (7):732–9. - PubMed
-
- Francia Pietro, Balla Cristina, Uccellini Arianna, Cappato Riccardo. Arrhythmia detection in single- and dual-chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillators: the more leads, the better? J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2009 Sep;20 (9):1077–82. - PubMed
-
- Stambler Bruce S. ICD arrhythmia detection and discrimination algorithms: whose is best? J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012 Apr;23 (4):367–9. - PubMed
-
- Theuns Dominic A M J, Rivero-Ayerza Maximo, Goedhart Dick M, Miltenburg Max, Jordaens Luc J. Morphology discrimination in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: consistency of template match percentage during atrial tachyarrhythmias at different heart rates. Europace. 2008 Sep;10 (9):1060–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
