Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease
- PMID: 29250494
- PMCID: PMC5729162
- DOI: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.4.211
Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease
Abstract
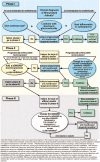
Arthritis damages the cartilage within joints, resulting in degenerative changes, including loss of function and joint instability. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the spine and bone-to-tendon attachment area within the sacroiliac joint leading to back pain and progressive spinal stiffness. In the final stages, AS causes hyperkyphosis-a condition closely tied to the human leukocyte antigen-B27 gene. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease characterized by the simultaneous inflammation of the synovium of multiple joints, leading to joint damage (e.g., destruction, deformation and disability). In the past, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARDs) have been used for the treatment of these autoimmune diseases, but biologic DMARDs have recently been introduced with excellent results. Gout is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes an alteration of joints resulting in severe pain. Specifically, gout is associated with an accumulation of uric acid within the body resulting from dysregulated purine metabolism, causing recurrent paroxysmal inflammation in the joints. Allopurinol and febuxostat are the primary treatment options for individuals with gout. It is necessary to have an accurate understanding of the pathogenesis, pathological ecology and treatment of AS, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis, which are the representative diseases that may cause inflammatory arthritis.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Gout; Reactive arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures



References
-
- Raychaudhuri SP, Deodhar A. The classification and diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:128–133. - PubMed
-
- Rostom S, Dougados M, Gossec L. New tools for diagnosing spondyloarthropathy. Joint Bone Spine. 2010;77:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Calin A, Porta J, Fries JF, Schurman DJ. Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA. 1977;237:2613–2614. - PubMed
-
- Chen HA, Chen CH, Liao HT, et al. Factors associated with radiographic spinal involvement and hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;40:552–558. - PubMed
-
- Vander Cruyssen B, Muñoz-Gomariz E, Font P, et al. Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: epidemiology and risk factors associated with hip replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49:73–81. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

