The effectiveness of a nurse-led illness perception intervention in COPD patients: a cluster randomised trial in primary care
- PMID: 29250529
- PMCID: PMC5722077
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00115-2016
The effectiveness of a nurse-led illness perception intervention in COPD patients: a cluster randomised trial in primary care
Abstract
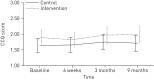
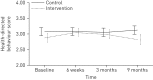
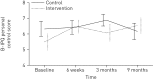
The new COPD-GRIP (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - Guidance, Research on Illness Perception) intervention translates evidence regarding illness perceptions and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) into a nurse intervention to guide COPD patients and to improve health outcomes. It describes how to assess and discuss illness perceptions in a structured way. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of the intervention in primary care. A cluster randomised controlled trial was conducted within 30 general practices and five home-care centres, including 204 COPD patients. 103 patients were randomly assigned to the intervention group and 101 patients to the usual-care group. To assess differences, repeated multilevel linear mixed modelling analyses were used. Primary outcome was change in health status on the Clinical COPD Questionnaire (CCQ) at 9 months. Secondary outcomes were HRQoL, daily activities, health education impact and changes in illness perceptions. There was no significant difference between the groups in the CCQ at 9 months. We found a significant increase in health-directed behaviour at 6 weeks (p=0.024) and in personal control (p=0.005) at 9 months in favour of the intervention group. The COPD-GRIP intervention, practised by nurses, did not improve health status in COPD patients in primary care. However, the intervention has benefits in improving the ability to control the disease and health-related behaviours in the short term. Therefore, taking illness perceptions into account when stimulating healthy behaviours in COPD patients should be considered. Further study on influencing the health status and HRQoL is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside this article at openres.ersjournals.com
Figures

References
-
- Decramer M, Janssens W. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and comorbidities. Lancet Respir Med 2013; 1: 73–83. - PubMed
-
- Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2013. Lancet 2015; 386: 743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- López-Campos JL, Tan W, Soriano JB. Global burden of COPD. Respirology 2016; 21: 14–23. - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2015 www.goldcopd.com Date last accessed: January 2016. Date last updated: January 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
