RNA Interference Screening to Identify Proliferation Determinants in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 29250574
- PMCID: PMC5730085
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2435
RNA Interference Screening to Identify Proliferation Determinants in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
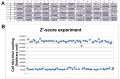
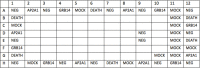
RNAi screening technology has revealed unknown determinants of various biological signaling pathways in biomedical studies. This protocol provided detailed information about how to use RNAi screening to identify proliferation determinants in breast tumor cells. siRNA-based libraries targeting against Estrogen receptor (ER)-network, including 631 genes relevant to estrogen signaling, was constructed for screening in breast cancer cells. Briefly, reverse transfection of siRNA induced transient gene knockdown in MCF7 cells. First, the transfection reagent for MCF7 cells was selected. Next, the Z'-score assay was used to monitor if screening conditions yielded efficiently. Then, the ER-network siRNA library screening was preceded by automatic machines under optimized experimental conditions.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CyBio automatic dispenser; Estrogen receptor (ER); Multidrop Combi-nL reagent dispenser; RNA interference (RNAi); Screening; WellMate microplate dispenser; Z′-score.
Figures



References
-
- Astsaturov I., Ratushny V., Sukhanova A., Einarson M. B., Bagnyukova T., Zhou Y., Devarajan K., Silverman J. S., Tikhmyanova N., Skobeleva N., Pecherskaya A., Nasto R. E., Sharma C., Jablonski S. A., Serebriiskii I. G., Weiner L. M. and Golemis E. A.(2010). Synthetic lethal screen of an EGFR-centered network to improve targeted therapies. Sci Signal 3(140): ra67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birmingham A., Selfors L. M., Forster T., Wrobel D., Kennedy C. J., Shanks E., Santoyo-Lopez J., Dunican D. J., Long A., Kelleher D., Smith Q., Beijersbergen R. L., Ghazal P. and Shamu C. E.(2009). Statistical methods for analysis of high-throughput RNA interference screens. Nat Methods 6(8): 569-575. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boutros M., Ahringer J.(2008). The art and design of genetic screens: RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet 9(7): 554-566. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J. H., Chung T. D. and Oldenburg K. R.(1999). A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4(2): 67-73. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

