Increased acetylcholine and glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex following intranasal orexin-A (hypocretin-1)
- PMID: 29250792
- PMCID: PMC5924451
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.14279
Increased acetylcholine and glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex following intranasal orexin-A (hypocretin-1)
Abstract
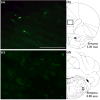
Orexin/hypocretin neurons of the lateral hypothalamus and perifornical area are integrators of physiological function. Previous work from our laboratory and others has shown the importance of orexin transmission in cognition. Age-related reductions in markers of orexin function further suggest that this neuropeptide may be a useful target for the treatment of age-related cognitive dysfunction. Intranasal administration of orexin-A (OxA) has shown promise as a therapeutic option for cognitive dysfunction. However, the neurochemical mechanisms of intranasal OxA administration are not fully understood. Here, we use immunohistochemistry and in vivo microdialysis to define the effects of acute intranasal OxA administration on: (i) activation of neuronal populations in the cortex, basal forebrain, and brainstem and (ii) acetylcholine (ACh) and glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of Fischer 344/Brown Norway F1 rats. Acute intranasal administration of OxA significantly increased c-Fos expression, a marker for neuronal activation, in the PFC and in subpopulations of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Subsequently, we investigated the effects of acute intranasal OxA on neurotransmitter efflux in the PFC and found that intranasal OxA significantly increased both ACh and glutamate efflux in this region. These findings were independent from any changes in c-Fos expression in orexin neurons, suggesting that these effects are not resultant from direct activation of orexin neurons. In total, these data indicate that intranasal OxA may enhance cognition through activation of distinct neuronal populations in the cortex and basal forebrain and through increased neurotransmission of ACh and glutamate in the PFC.
Keywords: acetylcholine; cognition; hypocretin; intranasal; microdialysis; orexin.
© 2017 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ammoun S, Holmqvist T, Shariatmadari R, Oonk HB, Detheux M, Parmentier M, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. Distinct recognition of OX1 and OX2 receptors by orexin peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Baier PC, Hallschmid M, Seeck-Hirschner M, Weinhold SL, Burkert S, Diessner N, Göder R, Aldenhoff JB, Hinze-Selch D. Effects of intranasal hypocretin-1 (orexin A) on sleep in narcolepsy with cataplexy. Sleep Med. 2011;12:941–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

