Phase I Study of ATR Inhibitor M6620 in Combination With Topotecan in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors
- PMID: 29252124
- PMCID: PMC5978471
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.6915
Phase I Study of ATR Inhibitor M6620 in Combination With Topotecan in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors
Abstract
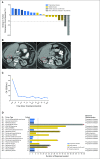
Purpose Our preclinical work identified depletion of ATR as a top candidate for topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) inhibitor synthetic lethality and showed that ATR inhibition sensitizes tumors to TOP1 inhibitors. We hypothesized that a combination of selective ATR inhibitor M6620 (previously VX-970) and topotecan, a selective TOP1 inhibitor, would be tolerable and active, particularly in tumors with high replicative stress. Patients and Methods This phase I study tested the combination of M6620 and topotecan in 3-week cycles using 3 + 3 dose escalation. The primary end point was the identification of the maximum tolerated dose of the combination. Efficacy and pharmacodynamics were secondary end points. Results Between September 2016 and February 2017, 21 patients enrolled. The combination was well tolerated, which allowed for dose escalation to the highest planned dose level (topotecan 1.25 mg/m2, days 1 to 5; M6620 210 mg/m2, days 2 and 5). One of six patients at this dose level experienced grade 4 thrombocytopenia that required transfusion, a dose-limiting toxicity. Most common treatment-related grade 3 or 4 toxicities were anemia, leukopenia, and neutropenia (19% each); lymphopenia (14%); and thrombocytopenia (10%). Two partial responses (≥ 18 months, ≥ 7 months) and seven stable disease responses ≥ 3 months (median, 9 months; range, 3 to 12 months) were seen. Three of five patients with small-cell lung cancer, all of whom had platinum-refractory disease, had a partial response or prolonged stable disease (10, ≥ 6, and ≥ 7 months). Pharmacodynamic studies showed preliminary evidence of ATR inhibition and enhanced DNA double-stranded breaks in response to the combination. Conclusion To our knowledge, this report is the first of an ATR inhibitor-chemotherapy combination. The maximum dose of topotecan plus M6620 is tolerable. The combination seems particularly active in platinum-refractory small-cell lung cancer, which tends not to respond to topotecan alone. Phase II studies with biomarker evaluation are ongoing.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02487095.
Figures


Comment in
-
Ataxia Telangiectasia-Mutated and Rad3-Related Inhibition and Topoisomerase I Trapping Create a Synthetic Lethality in Cancer Cells.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun 1;36(16):1628-1630. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.1857. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29369707 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Phase I Trial of First-in-Class ATR Inhibitor M6620 (VX-970) as Monotherapy or in Combination With Carboplatin in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep 20;38(27):3195-3204. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02404. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32568634 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 study of the ATR inhibitor berzosertib in combination with cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumours.Br J Cancer. 2021 Aug;125(4):520-527. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01406-w. Epub 2021 May 26. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34040174 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 study of the ATR inhibitor berzosertib (formerly M6620, VX-970) combined with gemcitabine ± cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumours.Br J Cancer. 2021 Aug;125(4):510-519. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01405-x. Epub 2021 May 26. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34040175 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I-II study of sequential administration of topotecan and oral etoposide (toposiomerase I and II inhibitors) in the treatment of patients with small cell lung carcinoma.Cancer. 2002 Oct 1;95(7):1511-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10836. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12237920 Clinical Trial.
-
Discovery of ATR kinase inhibitor berzosertib (VX-970, M6620): Clinical candidate for cancer therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Jun;210:107518. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107518. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32109490 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing cancer therapy: new frontiers in targeting DNA damage response.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1474337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1474337. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39372203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb;19(2):114-131. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00579-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34819622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multicellular Complex Tumor Spheroid Response to DNA Repair Inhibitors in Combination with DNA-damaging Drugs.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Aug 25;3(8):1648-1661. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0193. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37637936 Free PMC article.
-
RP-3500: A Novel, Potent, and Selective ATR Inhibitor that is Effective in Preclinical Models as a Monotherapy and in Combination with PARP Inhibitors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2022 Feb;21(2):245-256. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0615. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 34911817 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase II Single Arm Pilot Study of the CHK1 Inhibitor Prexasertib (LY2606368) in BRCA Wild-Type, Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2020 Dec;25(12):1013-e1824. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2020-0491. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32510664 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

