Antiepileptic drug use among women from the Taiwanese Registry of Epilepsy and Pregnancy: Obstetric complications and fetal malformation outcomes
- PMID: 29253023
- PMCID: PMC5734752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189497
Antiepileptic drug use among women from the Taiwanese Registry of Epilepsy and Pregnancy: Obstetric complications and fetal malformation outcomes
Abstract
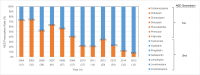
To investigate antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) prescription and pregnancy outcomes in pregnancies with epilepsy in Taiwan between 2004 and 2015. We retrospectively reviewed data from the Taiwanese Registry of Epilepsy and Pregnancy (TREP). The TREP registry is a voluntary prospective cohort registry, which tracks pregnant women with epilepsy and AED prescription throughout pregnancy, delivery, and early childhood development. All TREP pregnancies (n = 318) that had completed questionnaires up until delivery or had had an unsuccessful pregnancy were analyzed. Over 94.7% of women had been prescribed AEDs during pregnancy, with 69.0% and 25.7% having received monotherapy, or polytherapy, respectively. Among live births, 12 (3.9%) reported malformation. Cesarean section rate was reported higher than usual (54.5%). In 2004, 73.3% of AEDs prescribed were 1st generation, with 1st generation prescription rates falling to only 8.3% of total prescribed in 2015. AED polytherapy also fell during the study period (40.0% to 20.0%). Cesarean sections were found to be higher for women over 35 years, who had generalized epilepsy, or had experienced an obstetric complication during pregnancy term. Binary logistic regression revealed that Cesarean section was associated with maternal complications (OR = 5.11, CI 95% = 1.11-23.51, p = 0.036), while malformations were associated with obstetric complication (OR = 20.46, CI 95% = 4.80-87.21, p<0.001). Both AED risk types were not associated with complications or malformations. Our sample provides a unique insight into the women with epilepsy with AED use during pregnancy. Cesarean section rate was observed to be higher than usual, but malformation rates remained low. Results indicate a decrease in both 1st generation AEDs and proportion of patients receiving polytherapy over the study period. Obstetric complications were associated with Cesarean section. Fetal malformations were significantly associated with obstetric complications. AED risk factors were not significantly associated with either complications or malformations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- De Boer HM, Mula M, Sander JW (2008) The global burden and stigma of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 12: 540–546. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2007.12.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borthen I, Eide M, Daltveit A, Gilhus N (2011) Obstetric outcome in women with epilepsy: a hospital‐based, retrospective study. BJOG 118: 956–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.03004.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sveberg L, Svalheim S, Taubøll E (2015) The impact of seizures on pregnancy and delivery. Seizure 28: 35–38. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2015.02.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jadhav SV, Jadhav VK (2013) Comparative Study of Obstetric Outcome in Epileptic and Non-epileptic Pregnant Women. Ind Med Gaz: 352–355.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical