Adolescent cannabis use and brain systems supporting adult working memory encoding, maintenance, and retrieval
- PMID: 29253654
- PMCID: PMC6537905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.041
Adolescent cannabis use and brain systems supporting adult working memory encoding, maintenance, and retrieval
Abstract
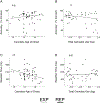
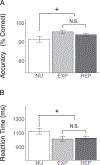
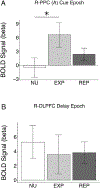
Given prior reports of adverse effects of cannabis use on working memory, an executive function with a protracted developmental course during adolescence, we examined associations between developmental patterns of cannabis use and adult working memory (WM) processes. Seventy-five adults with longitudinal assessments of cannabis use (60 with reported use, 15 with no reported use) and prenatal drug exposure assessment completed a spatial WM task during fMRI at age 28. All subjects passed a multi-drug urine screen on the day of testing and denied recreational drug use in the past week. A fast event-related design with partial trials was used to separate the BOLD response associated with encoding, maintenance, and retrieval periods of the WM task. Behavioral results showed that subjects who began using cannabis earlier in adolescence had longer reaction times (RT) than those with later initiation. Cannabis age of onset was further associated with reduced posterior parietal cortex (PPC) encoding BOLD activation, which significantly mediated age of onset WM RT associations. However, cannabis age of onset brain-behavior associations did not differ between groups with a single reported use and those with repeated use, suggesting age of onset effects may reflect substance use risk characteristics rather than a developmentally-timed cannabis exposure effect. Within repeated cannabis users, greater levels of total cannabis use were associated with performance-related increases in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) activation during maintenance. This pattern of significant results remained unchanged with inclusion of demographic and prenatal measures as covariates. Surprisingly, however, at the group level, cannabis users generally performed better than participants who reported never using cannabis (faster RT, higher accuracy). We extend previous investigations by identifying that WM associations with cannabis age of onset may be primary to PPC stimulus encoding activity, while the amount of cannabis use is associated with DLPFC maintenance processes. Poorer performance of participants who reported never using cannabis and the consistency of cannabis age of onset associations across single and repeated users limit interpretation of direct developmental effects of cannabis on WM in adulthood.
Keywords: Cannabis; Development; Executive function; Functional MRI; Substance use; Working memory.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosures
All authors report no financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Awh E, Jonides J, 2001. Overlapping mechanisms of attention and spatial working memory. Trends Cognit. Sci. 5 (3), 119–126. - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, 2013. lme4: Linear Mixed-effects Models Using S4 Classes. Retrieved from. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4.
-
- Chang L, Yakupov R, Cloak C, Ernst T, 2006. Marijuana use is associated with a reorganized visual-attention network and cerebellar hypoactivation. Brain 129 (5), 1096–1112. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Saad ZS, Adleman NE, Leibenluft E, Cox RW, 2015. Detecting the subtle shape differences in hemodynamic responses at the group level. Front. Neurosci. 9 Retrieved from. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4620161/. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

