High mobility group protein B1 is a predictor of poor survival in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 29254158
- PMCID: PMC5731868
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20538
High mobility group protein B1 is a predictor of poor survival in ovarian cancer
Abstract
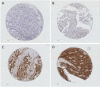
High-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) has been implicated in numerous tumour types where expression regulates tumour cell growth and survival. We hypothesised that high HMGB1 expression in ovarian tumours would predict poor patient survival. Using tissue microarrays of primary ovarian cancers combined with a comprehensive database of clinicopathological variables, the expression of HMGB1 was assessed by immunohistochemistry in two independent cohorts (n=194 and n=360) using a monoclonal antibody specific for HMGB1. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed an association of HMGB1 expression with progression free survival in the primary cohort (p=0.023). In the validation cohort, expression was associated with overall survival (p=0.002). Low expression of HMGB1 was protective and in a multivariate model HMGB1 expression was shown to be an independent predictor of poor survival in ovarian cancer (p=0.006). The role of HMGB1 in cancer is complex. As high levels of HMGB1 expression are likely to render ovarian cancer cells resistant to chemotherapy, therapies targeting the HMGB1 axis may be appropriate in the treatment of ovarian cancer patients.
Keywords: DAMP; HMGB1; autophagy; ovarian cancer; prognostic.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lowe KA, Chia VM, Taylor A, O’Malley C, Kelsh M, Mohamed M, Mowat FS, Goff B. An international assessment of ovarian cancer incidence and mortality. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130:107–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.03.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kang R, Tang D, Loze MT, Zeh HJ. Apoptosis to autophagy switch triggered by the MHC class III-encoded receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) Autophagy. 2011;7:91–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun X, Tang D. HMGB1-dependent and -independent autophagy. Autophagy. 2014;10:1873–6. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.32184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang D, Kang R, Cheh CW, Livesey KM, Liang X, Schapiro NE, Benschop R, Sparvero LJ, Amoscato AA, Tracey KJ, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT. HMGB1 release and redox regulates autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2010;29:5299–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.261. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Prasad R, Wilson SH. HMGB1: roles in base excision repair and related function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:119–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.11.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

