Transcription rate strongly affects splicing fidelity and cotranscriptionality in budding yeast
- PMID: 29254943
- PMCID: PMC5793784
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.225615.117
Transcription rate strongly affects splicing fidelity and cotranscriptionality in budding yeast
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Transcription rate strongly affects splicing fidelity and cotranscriptionality in budding yeast.Genome Res. 2018 Apr;28(4):606.2. doi: 10.1101/gr.236265.118. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 29610251 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
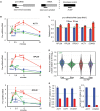
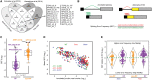
The functional consequences of alternative splicing on altering the transcription rate have been the subject of intensive study in mammalian cells but less is known about effects of splicing on changing the transcription rate in yeast. We present several lines of evidence showing that slow RNA polymerase II elongation increases both cotranscriptional splicing and splicing efficiency and that faster elongation reduces cotranscriptional splicing and splicing efficiency in budding yeast, suggesting that splicing is more efficient when cotranscriptional. Moreover, we demonstrate that altering the RNA polymerase II elongation rate in either direction compromises splicing fidelity, and we reveal that splicing fidelity depends largely on intron length together with secondary structure and splice site score. These effects are notably stronger for the highly expressed ribosomal protein coding transcripts. We propose that transcription by RNA polymerase II is tuned to optimize the efficiency and accuracy of ribosomal protein gene expression, while allowing flexibility in splice site choice with the nonribosomal protein transcripts.
© 2018 Aslanzadeh et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Alexander RD, Barrass JD, Dichtl B, Kos M, Obtulowicz T, Robert M-C, Koper M, Karkusiewicz I, Mariconti L, Tollervey D, et al. 2010a. RiboSys, a high-resolution, quantitative approach to measure the in vivo kinetics of pre-mRNA splicing and 3′-end processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA 16: 2570–2580. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ameur A, Zaghlool A, Halvardson J, Wetterbom A, Gyllensten U, Cavelier L, Feuk L. 2011. Total RNA sequencing reveals nascent transcription and widespread co-transcriptional splicing in the human brain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1435–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
