When do models of NeuroAIDS faithfully imitate "the real thing"?
- PMID: 29256039
- PMCID: PMC5910470
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-017-0601-5
When do models of NeuroAIDS faithfully imitate "the real thing"?
Abstract
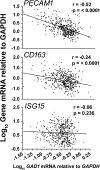
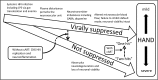
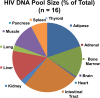
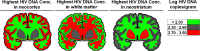
HIV-infected patients treated with antiretroviral medicines (ART) still face neurological challenges. HIV-associated neurocognitive disturbances (HAND) can occur, and latent viral DNA persisting in the central nervous system (CNS) prevents eradication of HIV. This communication focuses on how to develop experimental models of HAND and CNS HIV latency that best imitate the CNS pathophysiology in diseased humans, which we take to be "the real thing." Models of HIV encephalitis (HIVE) with active CNS viral replication were developed in the early years of the AIDS pandemic. The clinical relevancy of such models is in sharp decline because HIVE seldom occurs in virally suppressed patients, while HAND remains common. The search for improved models of HAND should incorporate the neurochemical, neuroimmunological and neuropathological features of virally suppressed patients. Common anomalies in these patients as established in autopsy brain specimens include brain endothelial cell activation and neurochemical imbalances of synaptic transmission; classical neurodegeneration may not be as crucial. With regard to latent HIV with viral suppression, human brain specimens show that the pool of latent proviral HIV DNA in the CNS is relatively small relative to the total body pool and does not change substantially over years. The CNS pool of latent virus probably differs from lymphoid tissues, because the mononuclear phagocyte system sustains productive infection (versus lymphocytes). These and yet-to-be discovered aspects of the human CNS of virally suppressed patients need to be better defined and addressed in experimental models. To maintain clinical relevancy, models of HAND and viral latency should faithfully emulate "the real thing."
Keywords: ART; CNS; Dementia; Eradication; HAND; HIV; Latency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ancuta P, Kamat A, Kunstman KJ, Kim E-Y, Autissier P, Wurcel A, Zaman T, Stone D, Mefford M, Morgello S, Singer EJ, Wolinsky SM, Gabuzda D. Microbial translocation is associated with increased monocyte activation and dementia in AIDS patients. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(6):e2516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology. 2007;69(18):1789–1799. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000287431.88658.8b. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck SE, Queen SE, Witwer KW, Metcalf Pate KA, Mangus LM, Gama L, Adams RJ, Clements JE, Zink MC, Mankowski JL. Paving the path to HIV neurotherapy: predicting CD4+ T cells. Cell host Microbe. 2015;16(6):711–721.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

