Resolving systematic errors in widely used enhancer activity assays in human cells
- PMID: 29256496
- PMCID: PMC5793997
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4534
Resolving systematic errors in widely used enhancer activity assays in human cells
Abstract
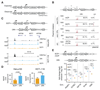
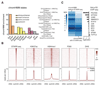
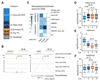
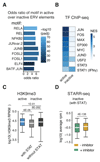
The identification of transcriptional enhancers in the human genome is a prime goal in biology. Enhancers are typically predicted via chromatin marks, yet their function is primarily assessed with plasmid-based reporter assays. Here, we show that such assays are rendered unreliable by two previously reported phenomena relating to plasmid transfection into human cells: (i) the bacterial plasmid origin of replication (ORI) functions as a conflicting core promoter and (ii) a type I interferon (IFN-I) response is activated. These cause confounding false positives and negatives in luciferase assays and STARR-seq screens. We overcome both problems by employing the ORI as core promoter and by inhibiting two IFN-I-inducing kinases, enabling genome-wide STARR-seq screens in human cells. In HeLa-S3 cells, we uncover strong enhancers, IFN-I-induced enhancers, and enhancers endogenously silenced at the chromatin level. Our findings apply to all episomal enhancer activity assays in mammalian cells and are key to the characterization of human enhancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shlyueva D, Stampfel G, Stark A. Transcriptional enhancers: from properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:272–286. - PubMed
-
- Saragosti S, Moyne G, Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980;20:65–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

