Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity
- PMID: 29257067
- PMCID: PMC6149725
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22122268
Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity
Abstract
The application of quinoline-based compounds for the treatment of malaria infections is hampered by drug resistance. Drug resistance has led to the combination of quinolines with other classes of antimalarials resulting in enhanced therapeutic outcomes. However, the combination of antimalarials is limited by drug-drug interactions. In order to overcome the aforementioned factors, several researchers have reported hybrid compounds prepared by reacting quinoline-based compounds with other compounds via selected functionalities. This review will focus on the currently reported quinoline-based hybrid compounds and their preclinical studies.
Keywords: 4-aminoquinoline; 8-aminoquinoline; hybrid compound; infectious disease; malaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



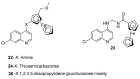

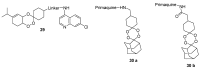

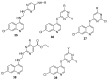
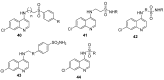
References
-
- Murugan K., Raichurkar A.V., Rahman F., Khan N., Iyer P.S. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel 8-aminoquinoline—Pyrazolopyrimidine hybrids as potent antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015;25:1100–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

