Amikacin: Uses, Resistance, and Prospects for Inhibition
- PMID: 29257114
- PMCID: PMC5889950
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22122267
Amikacin: Uses, Resistance, and Prospects for Inhibition
Abstract
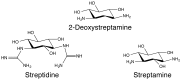
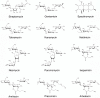
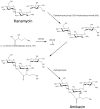
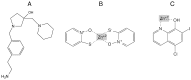
Aminoglycosides are a group of antibiotics used since the 1940s to primarily treat a broad spectrum of bacterial infections. The primary resistance mechanism against these antibiotics is enzymatic modification by aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes that are divided into acetyl-transferases, phosphotransferases, and nucleotidyltransferases. To overcome this problem, new semisynthetic aminoglycosides were developed in the 70s. The most widely used semisynthetic aminoglycoside is amikacin, which is refractory to most aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Amikacin was synthesized by acylation with the l-(-)-γ-amino-α-hydroxybutyryl side chain at the C-1 amino group of the deoxystreptamine moiety of kanamycin A. The main amikacin resistance mechanism found in the clinics is acetylation by the aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib [AAC(6')-Ib], an enzyme coded for by a gene found in integrons, transposons, plasmids, and chromosomes of Gram-negative bacteria. Numerous efforts are focused on finding strategies to neutralize the action of AAC(6')-Ib and extend the useful life of amikacin. Small molecules as well as complexes ionophore-Zn+2 or Cu+2 were found to inhibit the acetylation reaction and induced phenotypic conversion to susceptibility in bacteria harboring the aac(6')-Ib gene. A new semisynthetic aminoglycoside, plazomicin, is in advance stage of development and will contribute to renewed interest in this kind of antibiotics.
Keywords: amikacin; aminoglycoside modifying enzymes; aminoglycosides; antibiotic resistance; antisense.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Restoration of susceptibility to amikacin by 8-hydroxyquinoline analogs complexed to zinc.PLoS One. 2019 May 29;14(5):e0217602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217602. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31141575 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of aerobic gram-negative bacilli to aminoglycosides. Effects of 45 months of amikacin as first-line aminoglycoside therapy.Am J Med. 1986 Jun 30;80(6B):65-70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90481-x. Am J Med. 1986. PMID: 3014877
-
Characterization of mutants of the 6'-N-acetyltransferase encoded by the multiresistance transposon Tn1331: effect of Phen171-to-Leu171 and Tyr80-to-Cys80 substitutions.Plasmid. 1998;39(2):123-33. doi: 10.1006/plas.1997.1330. Plasmid. 1998. PMID: 9514709
-
Comparison of the next-generation aminoglycoside plazomicin to gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012 Apr;10(4):459-73. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.25. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012. PMID: 22512755 Review.
-
[Biochemical and genetic mechanisms for bacteria to acquire aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 May;55(5):1231-7. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9155180 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota intervention alleviates pulmonary inflammation in broilers exposed to fine particulate matter from broiler house.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 May 21;90(5):e0217423. doi: 10.1128/aem.02174-23. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38656183 Free PMC article.
-
Wollamide Cyclic Hexapeptides Synergize with Established and New Tuberculosis Antibiotics in Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0046523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00465-23. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37289062 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-functionalized UIO-66-NH2 for dual-drug delivery of vancomycin and amikacin against vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Nov 8;24(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03615-8. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39516717 Free PMC article.
-
The Adverse Effects of Tuberculosis Treatment: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 17;61(5):911. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050911. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Achyranthes aspera Extracts as Adjuvants for the Redressal of Antibiotic Resistance.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 18;14(10):2219. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102219. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serio A., Magalaes M., Blanchard J.S., Connolly L. Aminoglycosides: Mechanisms of action and resistance. In: Mayers D., Sobel J., Ouellette M., Kaye K., Marchaim D., editors. Antimicrobial Drug Resistance. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

