Evolutionary Proteomics Uncovers Ancient Associations of Cilia with Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 29257953
- PMCID: PMC5752135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.11.014
Evolutionary Proteomics Uncovers Ancient Associations of Cilia with Signaling Pathways
Abstract
Cilia are organelles specialized for movement and signaling. To infer when during evolution signaling pathways became associated with cilia, we characterized the proteomes of cilia from sea urchins, sea anemones, and choanoflagellates. We identified 437 high-confidence ciliary candidate proteins conserved in mammals and discovered that Hedgehog and G-protein-coupled receptor pathways were linked to cilia before the origin of bilateria and transient receptor potential (TRP) channels before the origin of animals. We demonstrated that candidates not previously implicated in ciliary biology localized to cilia and further investigated ENKUR, a TRP channel-interacting protein identified in the cilia of all three organisms. ENKUR localizes to motile cilia and is required for patterning the left-right axis in vertebrates. Moreover, mutation of ENKUR causes situs inversus in humans. Thus, proteomic profiling of cilia from diverse eukaryotes defines a conserved ciliary proteome, reveals ancient connections to signaling, and uncovers a ciliary protein that underlies development and human disease.
Keywords: GPCR; Hedgehog signaling; TRP channel; choanoflagellate; ciliopathy; cilium; left-right axis patterning; proteomics; sea anemone; sea urchin.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


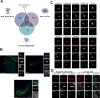


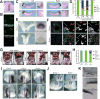
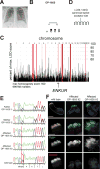
Comment in
-
Probing Cilia-Associated Signaling Proteomes in Animal Evolution.Dev Cell. 2017 Dec 18;43(6):653-655. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.12.009. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 29257946
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WOC, Cardon LR. GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics. 2001a;17:742–743. - PubMed
-
- Abecasis GAR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. Merlin: rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2001b;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Adamska M, Matus DQ, Adamski M, Green K, Rokhsar DS, Martindale MQ, Degnan BM. The evolutionary origin of hedgehog proteins. Curr Biol. 2007;17:R836–R837. - PubMed
-
- Afzelius BA. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science. 1976;193:317–319. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS Recommendations for Standardized Procedures for the Online and Offline Measurement of Exhaled Lower Respiratory Nitric Oxide and Nasal Nitric Oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:912–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

