Public Perceptions Regarding Use of Virtual Reality in Health Care: A Social Media Content Analysis Using Facebook
- PMID: 29258975
- PMCID: PMC5750416
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.7467
Public Perceptions Regarding Use of Virtual Reality in Health Care: A Social Media Content Analysis Using Facebook
Abstract
Background: Virtual reality (VR) technology provides an immersive environment that enables users to have modified experiences of reality. VR is increasingly used to manage patients with pain, disability, obesity, neurologic dysfunction, anxiety, and depression. However, public opinion regarding the use of VR in health care has not been explored. Understanding public opinion of VR is critical to ensuring effective implementation of this emerging technology.
Objective: This study aimed to examine public opinion about health care VR using social listening, a method that allows for the exploration of unfiltered views of topics discussed on social media and online forums.
Methods: In March 2016, NBC News produced a video depicting the use of VR for patient care. The video was repackaged by NowThis, a social media news website, and distributed on Facebook by Upworthy, a news aggregator, yielding 4.3 million views and 2401 comments. We used Microsoft Excel Power Query and ATLAS.ti software (version 7.5, Scientific Software Development) to analyze the comments using content analysis and categorized the comments around first-, second-, and third-order concepts. We determined self-identified gender from the user's Facebook page and performed sentiment analysis of the language to analyze whether the perception of VR differed by gender using a Pearson's chi-square test.
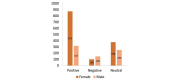
Results: Out of the 1614 analyzable comments, 1021 (63.26%) were attributed to female Facebook users, 572 (35.44%) to male users, and 21 (1.30%) to users of unknown gender. There were 1197 comments coded as expressing a positive perception about VR (74.16%), 251 coded as expressing a negative perception and/or concern (15.56%), and 560 coded as neutral (34.70%). Informants identified 20 use cases for VR in health care, including the use of VR for pain and stress reduction; bed-bound individuals; women during labor; and patients undergoing chemotherapy, dialysis, radiation, or imaging procedures. Negative comments expressed concerns about radiation, infection risk, motion sickness, and the ubiquity of and overall dependence on technology. There was a statistically significant association between the language valence of the Facebook post and the gender of the Facebook user; men were more likely to post negative perceptions about the use of VR for health care, whereas women were more likely to post positive perceptions (P<.001).
Conclusions: Most informants expressed positive perceptions about the use of VR in a wide range of health care settings. However, many expressed concerns that should be acknowledged and addressed as health care VR continues to evolve. Our results provide guidance in determining where further research on the use of VR in patient care is needed, and offer a formal opportunity for public opinion to shape the VR research agenda.
Keywords: qualitative research; social media; virtual reality.
©Michelle Sophie Keller, Hannah J Park, Maria Elena Cunningham, Joshua Eleazar Fouladian, Michelle Chen, Brennan Mason Ross Spiegel. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 19.12.2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Li A, Montaño Z, Chen VJ, Gold JI. Virtual reality and pain management: current trends and future directions. Pain Manag. 2011 Mar;1(2):147–57. doi: 10.2217/pmt.10.15. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21779307 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrougher GJ, Hoffman HG, Nakamura D, Lezotte D, Soltani M, Leahy L, Engrav LH, Patterson DR. The effect of virtual reality on pain and range of motion in adults with burn injuries. J Burn Care Res. 2009;30(5):785–91. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/19692911 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furman E, Jasinevicius TR, Bissada NF, Victoroff KZ, Skillicorn R, Buchner M. Virtual reality distraction for pain control during periodontal scaling and root planing procedures. J Am Dent Assoc. 2009 Dec;140(12):1508–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources