The CARMA3-Bcl10-MALT1 Signalosome Drives NFκB Activation and Promotes Aggressiveness in Angiotensin II Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29259013
- PMCID: PMC6436094
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1089
The CARMA3-Bcl10-MALT1 Signalosome Drives NFκB Activation and Promotes Aggressiveness in Angiotensin II Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
The angiotensin II receptor AGTR1, which mediates vasoconstrictive and inflammatory signaling in vascular disease, is overexpressed aberrantly in some breast cancers. In this study, we established the significance of an AGTR1-responsive NFκB signaling pathway in this breast cancer subset. We documented that AGTR1 overexpression occurred in the luminal A and B subtypes of breast cancer, was mutually exclusive of HER2 expression, and correlated with aggressive features that include increased lymph node metastasis, reduced responsiveness to neoadjuvant therapy, and reduced overall survival. Mechanistically, AGTR1 overexpression directed both ligand-independent and ligand-dependent activation of NFκB, mediated by a signaling pathway that requires the triad of CARMA3, Bcl10, and MALT1 (CBM signalosome). Activation of this pathway drove cancer cell-intrinsic responses that include proliferation, migration, and invasion. In addition, CBM-dependent activation of NFκB elicited cancer cell-extrinsic effects, impacting endothelial cells of the tumor microenvironment to promote tumor angiogenesis. CBM/NFκB signaling in AGTR1+ breast cancer therefore conspires to promote aggressive behavior through pleiotropic effects. Overall, our results point to the prognostic and therapeutic value of identifying AGTR1 overexpression in a subset of HER2-negative breast cancers, and they provide a mechanistic rationale to explore the repurposing of drugs that target angiotensin II-dependent NFκB signaling pathways to improve the treatment of this breast cancer subset.Significance: These findings offer a mechanistic rationale to explore the repurposing of drugs that target angiotensin action to improve the treatment of AGTR1-expressing breast cancers. Cancer Res; 78(5); 1225-40. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest:
S.A. Tomlins is a consultant for and receives honoraria from Roche/Ventana Medical Systems, Almac Diagnostics, Jansenn, AbbVie, Astellas/Medivation and Sanofi. S.A. Tomlins has sponsored research agreements with Compendia Biosciences/Life Technologies/ThermoFisher Scientific, Astellas and GenomeDX. D.R. Rhodes and S.A. Tomlins are Co-founders and equity holders in Strata Oncology. A.M. Chinnaiyan and D.R. Rhodes were Co-founders of Compendia Biosciences.
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures
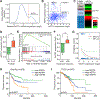
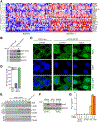
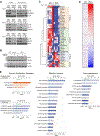

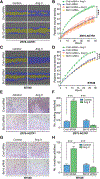
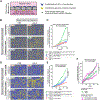
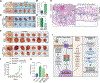
References
-
- Senkus E, Cardoso F, Pagani O. Time for more optimism in metastatic breast cancer? Cancer Treat Rev 2014;40:220–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

