Neural Progenitor Cell Polarity and Cortical Development
- PMID: 29259543
- PMCID: PMC5723293
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00384
Neural Progenitor Cell Polarity and Cortical Development
Abstract
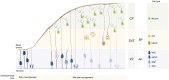
Neurons populating the cerebral cortex are generated during embryonic development from neural stem and progenitor cells in a process called neurogenesis. Neural stem and progenitor cells are classified into several classes based on the different location of mitosis (apical or basal) and polarity features (bipolar, monopolar and non-polar). The polarized architecture of stem cells is linked to the asymmetric localization of proteins, mRNAs and organelles, such as the centrosome and the Golgi apparatus (GA). Polarity affects stem cell function and allows stem cells to integrate environmental cues from distinct niches in the developing cerebral cortex. The crucial role of polarity in neural stem and progenitor cells is highlighted by the fact that impairment of cell polarity is linked to neurodevelopmental disorders such as Down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and schizophrenia.
Keywords: apical progenitors; basal progenitors; brain development; epithelial polarity; epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT); neural stem and progenitor cells; neurodevelopmental disorders; polarity.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

