Case Report: A rare cause of oral bullae: Angina bullosa hemorrhagica
- PMID: 29259770
- PMCID: PMC5728194
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.12977.1
Case Report: A rare cause of oral bullae: Angina bullosa hemorrhagica
Abstract
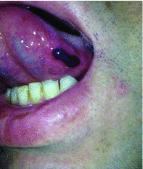
Angina bullosa hemorrhagica (ABH) is a benign disorder of the oral cavity. Clinically, oral, blood-filled blisters are seen. To give a proper diagnosis, one should rule out any other cause. We aim to present this case in order to emphasize this rare cause of oral bullae which is necessary to be differentiated from many serious dermatological and hematological disorders.
Keywords: Angina bullosa hemorrhagica; blister; oral mucosa.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources