Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of NAC transcription factor genes under abiotic stresses in radish (Raphanus sativus L.)
- PMID: 29259849
- PMCID: PMC5733918
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4172
Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of NAC transcription factor genes under abiotic stresses in radish (Raphanus sativus L.)
Abstract
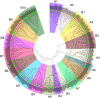
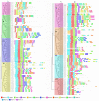
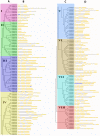
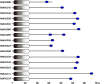
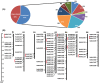
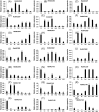
NAC (NAM, no apical meristem; ATAF, Arabidopsis transcription activation factor and CUC, cup-shaped cotyledon) proteins are among the largest transcription factor (TF) families playing fundamental biological processes, including cell expansion and differentiation, and hormone signaling in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. In this study, 172 RsNACs comprising 17 membrane-bound members were identified from the whole radish genome. In total, 98 RsNAC genes were non-uniformly distributed across the nine radish chromosomes. In silico analysis revealed that expression patterns of several NAC genes were tissue-specific such as a preferential expression in roots and leaves. In addition, 21 representative NAC genes were selected to investigate their responses to heavy metals (HMs), salt, heat, drought and abscisic acid (ABA) stresses using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). As a result, differential expressions among these genes were identified where RsNAC023 and RsNAC080 genes responded positively to all stresses except ABA, while RsNAC145 responded more actively to salt, heat and drought stresses compared with other genes. The results provides more valuable information and robust candidate genes for future functional analysis for improving abiotic stress tolerances in radish.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Expression profiling; Genome-wide analysis; NAC; Radish; Transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization of the AP2/ERF gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.): Unveiling evolution and patterns in response to abiotic stresses.Gene. 2019 Nov 15;718:144048. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144048. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31421189
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of the NAC genes under abiotic stresses in Cucumis sativus.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017 Apr;113:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.01.023. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28193581
-
Genome-wide characterization and evolutionary analysis of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs) to reveal their potential role under abiotic stresses in radish (Raphanus sativus L.).BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 24;20(1):772. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6121-3. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31651257 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization of the WRKY gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) reveals its critical functions under different abiotic stresses.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Nov;36(11):1757-1773. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2190-4. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28819820
-
Genome- and Transcriptome-Wide Characterization of bZIP Gene Family Identifies Potential Members Involved in Abiotic Stress Response and Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 16;20(24):6334. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246334. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31888167 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of NAC genes in Brassica juncea var. tumida.PeerJ. 2021 May 5;9:e11212. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11212. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33996278 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of NAC Domain Transcription Factor Genes of Tectona grandis L.f. Involved in Secondary Cell Wall Deposition.Genes (Basel). 2019 Dec 23;11(1):20. doi: 10.3390/genes11010020. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31878092 Free PMC article.
-
Early Response of Radish to Heat Stress by Strand-Specific Transcriptome and miRNA Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 6;20(13):3321. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133321. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31284545 Free PMC article.
-
Root Growth Adaptation to Climate Change in Crops.Front Plant Sci. 2020 May 8;11:544. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00544. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32457782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approaches Involved in the Vegetable Crops Salt Stress Tolerance Improvement: Present Status and Way Ahead.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 21;12:787292. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787292. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35281697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

