Pre-stroke glycemic control is associated with early neurologic deterioration in acute atrial fibrillation-related ischemic stroke
- PMID: 29260030
- PMCID: PMC5730912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2017.06.005
Pre-stroke glycemic control is associated with early neurologic deterioration in acute atrial fibrillation-related ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: It has been suggested that AF-related ischemic stroke (IS) that is accompanied by atherosclerotic burden have poorer outcomes. The aim of this study was to investigate the importance of pre-stroke glycemic control (PSGC) on the early neurologic deterioration (END) of patients with acute AF-related IS.
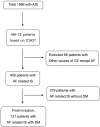
Methods: We retrospectively recruited 121 patients with AF-related IS who also had Diabetes mellitus (DM). The HbA1C level was measured in all subjects. END was defined as an increase in the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 4 NIHSS points within 7 days of symptom onset compared to the initial NIHSS score.
Results: In this study, 20.7% (25 patients) were classified as having a poor PSGC status with a HbA1C level above 8.0%. In the univariate analysis, a poor PSGC status (p < 0.01), smoking (p = 0.01), severe neurologic deficits at admission (p = 0.01), and a larger size of ischemic lesions on DWI (p < 0.01) were associated with the occurrence of END. In the multivariate model, a poor PSGC status (p = 0.02) and larger size of ischemic lesions on MRI (p < 0.01) were independent predictors of END in acute AF-related IS.
Conclusion: The HbA1c level upon admission was independently associated with significant prediction of END in acute AF-related IS.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Early neurologic deterioration; Stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene polymorphisms are associated with ischemic stroke severity and early neurologic deterioration in patients with atrial fibrillation.Brain Behav. 2019 Jun;9(6):e01291. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1291. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31012282 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and early neurological deterioration in stroke patients with and without atrial fibrillation.Heart Lung. 2020 Mar-Apr;49(2):193-197. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2019.10.009. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Heart Lung. 2020. PMID: 31699451
-
Prestroke glycemic control is associated with the functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke: the Fukuoka Stroke Registry.Stroke. 2011 Oct;42(10):2788-94. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.617415. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21817134
-
[Characteristics and outcome of acute ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Nov 17;95(43):3509-13. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26813274 Chinese.
-
Determinants of Use of Long-term Continuous Electrocardiographic Monitoring for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients without Atrial Fibrillation at Baseline.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(3):224-231. doi: 10.2174/1567202617666200423092025. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 32324514
Cited by
-
Interpretable machine learning for early neurological deterioration prediction in atrial fibrillation-related stroke.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 18;11(1):20610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99920-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34663874 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Conundrums in the Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in the Elderly.J Transl Int Med. 2019 Mar 29;7(1):10-14. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0003. eCollection 2019 Mar. J Transl Int Med. 2019. PMID: 30997351 Free PMC article.
-
High HbA1c is associated with decreased 6-month survival and poor outcomes after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a retrospective cohort study.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2020 Sep 3;28(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13049-020-00782-1. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32883318 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable Machine Learning Model Predicting Early Neurological Deterioration in Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Retrospective Study.Brain Sci. 2023 Mar 26;13(4):557. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040557. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han S.W., Nam H.S., Kim S.H. Frequency and significance of cardiac sources of embolism in the TOAST clas-sification. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007;24:463–468. - PubMed
-
- Lin S., Wu B., Hao Z.L. Characteristics, treatment and outcome of ischemic stroke with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese hospital-based stroke study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011;31(5):419–426. - PubMed
-
- Puwanant S., Varr B.C., Shrestha K. Role of the CHADS2 score in the evaluation of thromboembolic risk in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing transe-sophageal echocardiography before pulmonary vein isolation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;54:2032–2039. - PubMed
-
- Rader V.J., Khumri T.M., Idupulapati M. Clinical predictors of left atrial thrombus and spontaneous echocardiographic contrast in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2007;20:1181–1185. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources