Baohuoside-I suppresses cell proliferation and migration by up-regulating miR-144 in melanoma
- PMID: 29260980
- PMCID: PMC6130571
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1418391
Baohuoside-I suppresses cell proliferation and migration by up-regulating miR-144 in melanoma
Abstract
Context: Baohuoside-I was reported to induce apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer and inhibit the growth of multiple myeloma cells. The antitumour potential of baohuoside-I has not been demonstrated in melanoma yet.
Objective: To investigate the potential antitumour activity of baohuoside-I against melanoma and elucidate its underlying molecular mechanism.
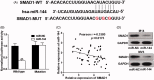
Materials and methods: Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay. The malignant invasion capacity was measured with trans-well assay. The relative expression change of microRNAs was profiled with microarray. TargetScan was utilized for prediction of target gene of miR-144. Regulatory effect of miR-144 on SMAD1 was determined by dual luciferase reporter assay. Endogenous SMAD1 protein in response to ectopic expression of miR-144 was determined by immunoblotting. Xenograft mice were employed to evaluate antitumour potential of baohuoside-I (25 mg/kg by tail intravenous injection every two days) in vivo.
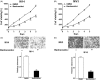
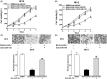
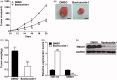
Results: Baohuoside-I significantly inhibited proliferation (45 ± 4% reduction in M14 and 35 ± 3% reduction in MV3 at 24 h) and migration (70 ± 4% reduction in M14 and 72 ± 3% reduction in MV3) in melanoma cells. Mechanistically, baohuoside-I up-regulated miR-144 expression levels (3 ± 0.2-fold). Silence of miR-144 reversed the inhibition of baohuoside-I in melanoma. We have identified that SMAD1 was the novel target of miR-144. Moreover, baohuoside-I suppressed melanoma in vivo (52 ± 8% reduction in xenograft tumour size at day 20).
Conclusions: Our data suggested significant antitumour potential of baohuoside-I against melanoma both in vitro and in vivo, which warrants further laboratory investigation and clinical trial.
Keywords: Antitumour effects; SMAD1; invasion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The flavonoid Baohuoside-I inhibits cell growth and downregulates survivin and cyclin D1 expression in esophageal carcinoma via β-catenin-dependent signaling.Oncol Rep. 2011 Nov;26(5):1149-56. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1400. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21785828
-
Isoliquiritigenin suppresses human melanoma growth by targeting miR-301b/LRIG1 signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 6;37(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0844-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30081934 Free PMC article.
-
miR-let-7b and miR-let-7c suppress tumourigenesis of human mucosal melanoma and enhance the sensitivity to chemotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 22;38(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1190-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31118065 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of baohuoside-I on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Apr;40(4):566-576. doi: 10.1177/0960327120960765. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32945196
-
MicroRNA-365 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant melanoma by targeting NRP1 expression.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4913-22. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191184 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Baohuoside I via mTOR Apoptotic Signaling to Inhibit Glioma Cell Growth.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 10;12:11435-11444. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S265803. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33204156 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of Natural Compounds from Chinese Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Melanoma.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025 Jul;26(7):533-568. doi: 10.1007/s11864-025-01322-8. Epub 2025 May 15. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40372659 Review.
-
MicroRNA-144: A novel biological marker and potential therapeutic target in human solid cancers.J Cancer. 2020 Sep 25;11(22):6716-6726. doi: 10.7150/jca.46293. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33046994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of microRNA-144-5p on the proliferation, invasion and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by targeting SMAD1.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jan;19(1):165-171. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8194. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31853287 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and Therapeutic Potential of a Natural Flavonoid Icariside II in Human Complication.Curr Drug Targets. 2025;26(5):320-330. doi: 10.2174/0113894501329810241117231839. Curr Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39757637 Review.
References
-
- Ambros V.2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bao H, Li X, Li H, Xing H, Xu B, Zhang X, Liu Z.. 2017. MicroRNA-144 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting ZFX. J Biosci. 42:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Choi HJ, Eun J-S, Kim DK, Li RH, Shin T-Y, Park H, Cho N-P, Soh Y.. 2008. Icariside II from Epimedium koreanum inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in human osteosarcoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 579:58–65. - PubMed
-
- Friedman RJ, Rigel DS, Kopf AW.. 1985. Early detection of malignant melanoma: the role of physician examination and self-examination of the skin. CA Cancer J Clin. 35:130–151. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
