PEGylation of zinc nanoparticles amplifies their ability to enhance olfactory responses to odorant
- PMID: 29261701
- PMCID: PMC5738065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189273
PEGylation of zinc nanoparticles amplifies their ability to enhance olfactory responses to odorant
Abstract
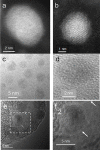
Olfactory responses are intensely enhanced with the addition of endogenous and engineered primarily-elemental small zinc nanoparticles (NPs). With aging, oxidation of these Zn nanoparticles eliminated the observed enhancement. The design of a polyethylene glycol coating to meet storage requirements of engineered zinc nanoparticles is evaluated to achieve maximal olfactory benefit. The zinc nanoparticles were covered with 1000 g/mol or 400 g/mol molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG). Non-PEGylated and PEGylated zinc nanoparticles were tested by electroolfactogram with isolated rat olfactory epithelium and odorant responses evoked by the mixture of eugenol, ethyl butyrate and (±) carvone after storage at 278 K (5 oC), 303 K (30 oC) and 323 K (50 oC). The particles were analyzed by atomic force microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and laser Doppler velocimetry. Our data indicate that stored ZnPEG400 nanoparticles maintain physiologically-consistent olfactory enhancement for over 300 days. These engineered Nanoparticles support future applications in olfactory research, sensitive detection, and medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




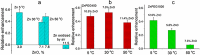
References
-
- Samoylov AM, Samoylova TI, Pustovyy OM, Samoylov AA, Toivio-Kinnucan MA, Morrison NE, et al. Novel Metal Clusters Isolated from Blood Are Lethal to Cancer Cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005;179(3):115–24. doi: 10.1159/000085003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Viswaprakash N, Dennis JC, Globa L, Pustovyy O, Josephson EM, Kanju P, et al. Enhancement of Odorant-Induced Response in Olfactory Receptor Neurons by Zinc Nanoparticles. Chem Senses. 2009;34:547–57. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjp031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jia H, Pustovyy OM, Wang Y, Waggoner P, Beyers RJ, Schumacher J, et al. Enhancement of Odor-Induced Activity in the Canine Brain by Zinc Nanoparticles: A Functional MRI Study in Fully Unrestrained Conscious Dogs. Chem Senses. 2016;41(1):53–67. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv054 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hagerty S, Daniels Y, Singletary M, Pustovyy O, Globa L, MacCrehan WA, et al. After oxidation, zinc nanoparticles lose their ability to enhance responses to odorants. Biometals 2016;29(6):1005–18. doi: 10.1007/s10534-016-9972-y - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

