Combination of palbociclib with enzalutamide shows in vitro activity in RB proficient and androgen receptor positive triple negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29261702
- PMCID: PMC5737960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189007
Combination of palbociclib with enzalutamide shows in vitro activity in RB proficient and androgen receptor positive triple negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
Objectives: Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks specific drug targets and remains challenging. Palbociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor is approved for metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive and human epithermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer. The nature of cell cycle inhibition by palbociclib suggests its potential in TNBC cells. Retinoblastoma (RB, a known substrate of CDK4/6) pathway deregulation is a frequent occurrence in TNBC and studies have revealed that pharmacological CDK4/6 inhibition induces a cooperative cytostatic effect with doxorubicin in RB-proficient TNBC models. In addition, recent studies reported that anti-androgen therapy shows preclinical efficacy in androgen-receptor (AR)-positive TNBC cells. Here we examined the effect of palbociclib in combination with an anti-androgen enzalutamide in TNBC cells.
Method: MDA-MB-453, BT-549, MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 TNBC cell lines were used for in vitro studies. Protein expressions were assessed by Western blot analysis. Cytostatic effect was examined by MTT assay. Cell cycle and apoptosis were examined by flow cytometry.
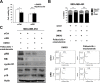
Results: Palbociclib showed inhibitory effect in RB-proficient TNBC cells, and enzalutamide inhibited cell viability in AR-positive TNBC cells. Enzalutamide treatment could enhance the palbociclib-induced cytostatic effect in AR-positive/RB-proficient TNBC cells. In addition, palbociclib-mediated G1 arrest in AR-positive/RB-proficient TNBC cells was attenuated by RB knockdown.
Conclusion: Our study provided a preclinical rationale in selecting patients who might have therapeutic benefit from combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with AR antagonists.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Gelmon K, Dent R, Mackey JR, Laing K, McLeod D, Verma S. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer: optimising therapeutic outcomes. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(9):2223–34. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds067 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi K, Ito Y, Matsuura M, Fukada I, Horii R, Takahashi S, et al. Impact of immunohistological subtypes on the long-term prognosis of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Surg Today. 2016;46(7):821–6. doi: 10.1007/s00595-015-1252-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Malorni L, Shetty PB, De Angelis C, Hilsenbeck S, Rimawi MF, Elledge R, et al. Clinical and biologic features of triple-negative breast cancers in a large cohort of patients with long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136(3):795–804. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2315-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mayer IA, Abramson VG, Lehmann BD, Pietenpol JA. New strategies for triple-negative breast cancer—deciphering the heterogeneity. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(4):782–90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0583 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toogood PL, Harvey PJ, Repine JT, Sheehan DJ, VanderWel SN, Zhou H, et al. Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. J Med Chem. 2005;48(7):2388–406. doi: 10.1021/jm049354h - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

