Efficient visible light photocatalysis of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) in aqueous solutions using supported zinc oxide nanorods
- PMID: 29261711
- PMCID: PMC5738043
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189276
Efficient visible light photocatalysis of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) in aqueous solutions using supported zinc oxide nanorods
Abstract
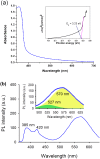
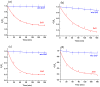
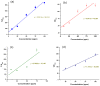
Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes (BTEX) are some of the common environmental pollutants originating mainly from oil and gas industries, which are toxic to human as well as other living organisms in the ecosystem. Here we investigate photocatalytic degradation of BTEX under visible light irradiation using supported zinc oxide (ZnO) nanorods grown on glass substrates using a microwave assisted hydrothermal method. ZnO nanorods were characterized by electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), specific surface area, UV/visible absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy. Visible light photocatalytic degradation products of BTEX are studied for individual components using gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS). ZnO nanorods with significant amount of electronic defect states, due to the fast crystallization of the nanorods under microwave irradiation, exhibited efficient degradation of BTEX under visible light, degrading more than 80% of the individual BTEX components in 180 minutes. Effect of initial concentration of BTEX as individual components is also probed and the photocatalytic activity of the ZnO nanorods in different conditions is explored. Formation of intermediate byproducts such as phenol, benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde and benzoic acid were confirmed by our HPLC analysis which could be due to the photocatalytic degradation of BTEX. Carbon dioxide was evaluated and showed an increasing pattern over time indicating the mineralization process confirming the conversion of toxic organic compounds into benign products.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Fernandez-Lima FA, Becker C, McKenna AM, Rodgers RP, Marshall AG, et al. (2009) Petroleum Crude Oil Characterization by IMS-MS and FTICR MS. Anal Chem 81: 9941–9947. doi: 10.1021/ac901594f - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klein GC, Angström A, Rodgers RP, Marshall AG (2006) Use of Saturates/Aromatics/Resins/Asphaltenes (SARA) Fractionation To Determine Matrix Effects in Crude Oil Analysis by Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 20: 668–672.
-
- Hughey CA, Rodgers RP, Marshall AG (2002) Resolution of 11 000 Compositionally Distinct Components in a Single Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrum of Crude Oil. Anal Chem 74: 4145–4149. - PubMed
-
- Bamberger M, Oswald RE (2015) Long-term impacts of unconventional drilling operations on human and animal health. J Environ Sci Health, Part A 50: 447–459. - PubMed
-
- do Rego ECP, Pereira Netto AD (2007) PAHs and BTEX in Groundwater of Gasoline Stations from Rio de Janeiro City, Brazil. Bull of EnvironContam Toxicol 79: 660–664. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

