Potential for therapeutic targeting of AKAP signaling complexes in nervous system disorders
- PMID: 29262295
- PMCID: PMC5899024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.12.004
Potential for therapeutic targeting of AKAP signaling complexes in nervous system disorders
Abstract
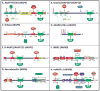
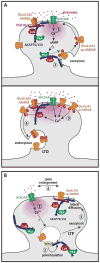
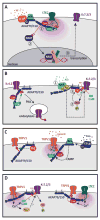
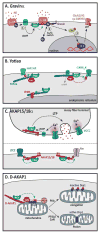
A common feature of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders is a breakdown in the integrity of intracellular signal transduction pathways. Dysregulation of ion channels and receptors in the cell membrane and the enzymatic mediators that link them to intracellular effectors can lead to synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death. However, therapeutic targeting of these ubiquitous signaling elements can lead to off-target side effects due to their widespread expression in multiple systems of the body. A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) are multivalent scaffolding proteins that compartmentalize a diverse range of receptor and effector proteins to streamline signaling within nanodomain signalosomes. A number of essential neurological processes are known to critically depend on AKAP-directed signaling and an understanding of the role AKAPs play in nervous system disorders has emerged in recent years. Selective targeting of AKAP protein-protein interactions may be a means to uncouple pathologically active signaling pathways in neurological disorders with a greater degree of specificity. In this review we will discuss the role of AKAPs in both regulating normal nervous system function and dysfunction associated with disease, and the potential for therapeutic targeting of AKAP signaling complexes.
Keywords: AKAP; Calcium; Ion channel; Nervous system; PKA; cAMP.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abrenica B, AlShaaban M, Czubryt MP. The A-kinase anchor protein AKAP121 is a negative regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2009;46:674–681. - PubMed
-
- Adams JP, Dudek SM. Late-phase long-term potentiation: getting to the nucleus. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2005;6:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Affaitati A, Cardone L, de Cristofaro T, Carlucci A, Ginsberg MD, Varrone S, Gottesman ME, Avvedimento EV, Feliciello A. Essential role of A-kinase anchor protein 121 for cAMP signaling to mitochondria. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:4286–4294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

