Systemic Messenger RNA Therapy as a Treatment for Methylmalonic Acidemia
- PMID: 29262333
- PMCID: PMC9667413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.081
Systemic Messenger RNA Therapy as a Treatment for Methylmalonic Acidemia
Erratum in
-
Systemic Messenger RNA Therapy as a Treatment for Methylmalonic Acidemia.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 28;24(9):2520. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.049. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30157442 No abstract available.
Abstract
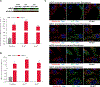
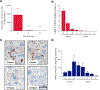
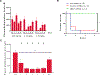
Isolated methylmalonic acidemia/aciduria (MMA) is a devastating metabolic disorder with poor outcomes despite current medical treatments. Like other mitochondrial enzymopathies, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is not available, and although promising, AAV gene therapy can be limited by pre-existing immunity and has been associated with genotoxicity in mice. To develop a new class of therapy for MMA, we generated a pseudoU-modified codon-optimized mRNA encoding human methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (hMUT), the enzyme most frequently mutated in MMA, and encapsulated it into biodegradable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Intravenous (i.v.) administration of hMUT mRNA in two different mouse models of MMA resulted in a 75%-85% reduction in plasma methylmalonic acid and was associated with increased hMUT protein expression and activity in liver. Repeat dosing of hMUT mRNA reduced circulating metabolites and dramatically improved survival and weight gain. Additionally, repeat i.v. dosing did not increase markers of liver toxicity or inflammation in heterozygote MMA mice.
Keywords: lipid nanoparticle; liver; mRNA therapy; methylmalonic acid; methylmalonic acidemia/aciduria; methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
D.A., A.F., S.L., X.Z., J.P., M.T., S.H., J.Z., R.R., B.L., R.H., G.B., V.P., S.S., K.E.M., E.S.K., T.S., C.M., C.L., L.T.G., and P.G.V.M. are employees of, and receive salary and stock options from, Moderna Therapeutics. J.L.S., R.J.C., and C.P.V. declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Authoring Committee (2008). Newborn screening expands: recommendations for pediatricians and medical homes–implications for the system. Pediatrics 121, 192–217. - PubMed
-
- Baba M, Itaka K, Kondo K, Yamasoba T, and Kataoka K. (2015). Treatment of neurological disorders by introducing mRNA in vivo using polyplex nanomicelles. J. Control. Release 201, 41–48. - PubMed
-
- Barros SA, and Gollob JA (2012). Safety profile of RNAi nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 64, 1730–1737. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

