PHIP - a novel candidate breast cancer susceptibility locus on 6q14.1
- PMID: 29262523
- PMCID: PMC5732689
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21800
PHIP - a novel candidate breast cancer susceptibility locus on 6q14.1
Abstract
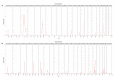
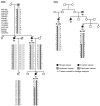
Most non-BRCA1/2 breast cancer families have no identified genetic cause. We used linkage and haplotype analyses in familial and sporadic breast cancer cases to identify a susceptibility locus on chromosome 6q. Two independent genome-wide linkage analysis studies suggested a 3 Mb locus on chromosome 6q and two unrelated Swedish families with a LOD >2 together seemed to share a haplotype in 6q14.1. We hypothesized that this region harbored a rare high-risk founder allele contributing to breast cancer in these two families. Sequencing of DNA and RNA from the two families did not detect any pathogenic mutations. Finally, 29 SNPs in the region were analyzed in 44,214 cases and 43,532 controls from BCAC, and the original haplotypes in the two families were suggested as low-risk alleles for European and Swedish women specifically. There was also some support for one additional independent moderate-risk allele in Swedish familial samples. The results were consistent with our previous findings in familial breast cancer and supported a breast cancer susceptibility locus at 6q14.1 around the PHIP gene.
Keywords: familial breast cancer; linkage analysis; risk haplotype; sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Pukkala E, Skytthe A, Hemminki K. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer—analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:78–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200007133430201. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hall JM, Lee MK, Newman B, Morrow JE, Anderson LA, Huey B, King MC. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990;250:1684–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

