Microtubins: a novel class of small synthetic microtubule targeting drugs that inhibit cancer cell proliferation
- PMID: 29262617
- PMCID: PMC5732783
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21945
Microtubins: a novel class of small synthetic microtubule targeting drugs that inhibit cancer cell proliferation
Abstract
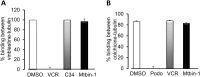
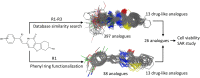
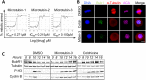
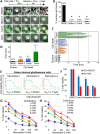
Microtubule targeting drugs like taxanes, vinca alkaloids, and epothilones are widely-used and effective chemotherapeutic agents that target the dynamic instability of microtubules and inhibit spindle functioning. However, these drugs have limitations associated with their production, solubility, efficacy and unwanted toxicities, thus driving the need to identify novel antimitotic drugs that can be used as anticancer agents. We have discovered and characterized the Microtubins (Microtubule inhibitors), a novel class of small synthetic compounds, which target tubulin to inhibit microtubule polymerization, arrest cancer cells predominantly in mitosis, activate the spindle assembly checkpoint and trigger an apoptotic cell death. Importantly, the Microtubins do not compete for the known vinca or colchicine binding sites. Additionally, through chemical synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies, we have determined that specific modifications to the Microtubin phenyl ring can activate or inhibit its bioactivity. Combined, these data define the Microtubins as a novel class of compounds that inhibit cancer cell proliferation by perturbing microtubule polymerization and they could be used to develop novel cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: cancer cell proliferation; cell cycle; cell division; microtubules; tubulin-targeting agents.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST S.S., Y-C.L., R.D. and J.Z.T. are authors on a pending patent on the Microtubins. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Lansing TJ, McConnell RT, Duckett DR, Spehar GM, Knick VB, Hassler DF, Noro N, Furuta M, Emmitte KA, Gilmer TM, Mook RA, Jr, Cheung M. In vitro biological activity of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:450–59. - PubMed
-
- Gascoigne KE, Taylor SS. Cancer cells display profound intra- and interline variation following prolonged exposure to antimitotic drugs. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:111–22. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

