hsa-miR-29c-3p regulates biological function of colorectal cancer by targeting SPARC
- PMID: 29262657
- PMCID: PMC5732823
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22356
hsa-miR-29c-3p regulates biological function of colorectal cancer by targeting SPARC
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most common type of behavioral cancers, miRNAs play a critical role in cancer development and progression. In the present study, we downloaded the original data from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and conduct data analysis. has-mir-29c-3p mimic, inhibitor, negative control or si-SPARC (secreted protein acidic, rich in cysteine) were transfected into HCT116 cells, respectively. Quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure has-mir-29c-3p and SPARC mRNA expressions, western blot was used to detect ACAA1 (acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 1), ACOX1 (acyl-CoA oxidase 1), COL1A1(collagen, type I, alpha-1), COL1A2 (collagen, type I, alpha-2), COL4A1 (collagen, type IV, alpha-1), COL5A2 (collagen, type V, alpha-2), COL12A1 (collagen, type XII, alpha-1), CPT2 (carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2), ETHE1 (persulfide dioxygenase), HMGCS2 (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2), SPARC, SQRDL (sulfide quinone oxidoreductase), and TST (thiosulfate sulfurtransferase) protein expression. CCK-8 and wound healing assay were employed to verify cell proliferation and migration. The luciferase reporter assay data made sure the target correlation of has-mir-29c-3p and SPARC. Firstly, we found that the expression of has-mir-29c-3p was lower in CRC tissues than in their paired corresponding non-cancerous tissues and there was significant inversed correlation between has-mir-29c-3p and SPARC. Overexpression of has-mir-29c-3p reduced cell proliferation and migration. SPARC was identified as a direct target of has-mir-29c-3p, whose silencing reduced cell proliferation and migration. These data showed that has-mir-29c-3p regulates CRC cell functions through regulating SPARC expression. Taken together, has-mir-29c-3p may function as an oncogenic miRNA targeting SPARC, targeted modulation of has-mir-29c-3p expression may became a potential strategy for the treatment.
Keywords: SPARC; colorectal cancer; hsa-miR-29c-3p; migration; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

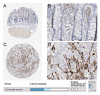



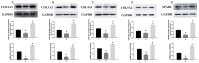


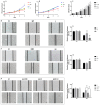
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20107. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1490–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61649-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marmol I, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010197. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brody H. Colorectal cancer. Nature. 2015;521:S1. https://doi.org/10.1038/521S1a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shi S, Yang J, Sun D. CT-guided 125I brachytherapy on pulmonary metastases after resection of colorectal cancer: A report of six cases. Oncol Lett. 2015;9:375–80. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.2649. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

