Investigating the genetic architecture of dementia with Lewy bodies: a two-stage genome-wide association study
- PMID: 29263008
- PMCID: PMC5805394
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30400-3
Investigating the genetic architecture of dementia with Lewy bodies: a two-stage genome-wide association study
Abstract
Background: Dementia with Lewy bodies is the second most common form of dementia in elderly people but has been overshadowed in the research field, partly because of similarities between dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease. So far, to our knowledge, no large-scale genetic study of dementia with Lewy bodies has been done. To better understand the genetic basis of dementia with Lewy bodies, we have done a genome-wide association study with the aim of identifying genetic risk factors for this disorder.
Methods: In this two-stage genome-wide association study, we collected samples from white participants of European ancestry who had been diagnosed with dementia with Lewy bodies according to established clinical or pathological criteria. In the discovery stage (with the case cohort recruited from 22 centres in ten countries and the controls derived from two publicly available database of Genotypes and Phenotypes studies [phs000404.v1.p1 and phs000982.v1.p1] in the USA), we performed genotyping and exploited the recently established Haplotype Reference Consortium panel as the basis for imputation. Pathological samples were ascertained following autopsy in each individual brain bank, whereas clinical samples were collected after participant examination. There was no specific timeframe for collection of samples. We did association analyses in all participants with dementia with Lewy bodies, and also only in participants with pathological diagnosis. In the replication stage, we performed genotyping of significant and suggestive results from the discovery stage. Lastly, we did a meta-analysis of both stages under a fixed-effects model and used logistic regression to test for association in each stage.
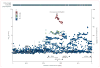
Findings: This study included 1743 patients with dementia with Lewy bodies (1324 with pathological diagnosis) and 4454 controls (1216 patients with dementia with Lewy bodies vs 3791 controls in the discovery stage; 527 vs 663 in the replication stage). Results confirm previously reported associations: APOE (rs429358; odds ratio [OR] 2·40, 95% CI 2·14-2·70; p=1·05 × 10-48), SNCA (rs7681440; OR 0·73, 0·66-0·81; p=6·39 × 10-10), an GBA (rs35749011; OR 2·55, 1·88-3·46; p=1·78 × 10-9). They also provide some evidence for a novel candidate locus, namely CNTN1 (rs7314908; OR 1·51, 1·27-1·79; p=2·32 × 10-6); further replication will be important. Additionally, we estimate the heritable component of dementia with Lewy bodies to be about 36%.
Interpretation: Despite the small sample size for a genome-wide association study, and acknowledging the potential biases from ascertaining samples from multiple locations, we present the most comprehensive and well powered genetic study in dementia with Lewy bodies so far. These data show that common genetic variability has a role in the disease.
Funding: The Alzheimer's Society and the Lewy Body Society.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures

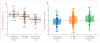

Comment in
-
The genetic architecture of dementia with Lewy bodies is shaping up.Lancet Neurol. 2018 Jan;17(1):25-26. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30411-8. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Lancet Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29262999 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bogaerts V, Engelborghs S, Kumar-Singh S, et al. A novel locus for dementia with Lewy bodies: a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder. Brain. 2007;130:2277–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 DA019706/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P005748/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS038377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L022656/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_G1000734/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 200/ALZS_/Alzheimer's Society/United Kingdom
- R01 NS078086/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 203249/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 NS100600/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N012453/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000951/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 CA084724/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060113/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L023784/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000951/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L016397/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA NS003154/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

