Dramatic Increase of Amoxicillin-Induced Crystal Nephropathy Found in a Cohort Study of French Pharmacovigilance Centers
- PMID: 29263078
- PMCID: PMC5826165
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01630-17
Dramatic Increase of Amoxicillin-Induced Crystal Nephropathy Found in a Cohort Study of French Pharmacovigilance Centers
Abstract
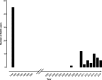
An increase in amoxicillin-induced crystal nephropathy (AICN) incidence has been recently suggested. The aims of this study were to investigate the trend of AICN incidence through Paris' regional centers of pharmacovigilance (Paris RCPVs) and better describe this rare adverse drug reaction. Forty-five AICN cases were identified between 1985 and 2016. All cases, except one, were reported since 2010. Amoxicillin (AMX) was administered intravenously (65 [interquartile range {IQR}, 43 to 110] mg/kg of body weight/day) in all patients, either for treating infection (n = 15) or as surgical prophylaxis (n = 30). Delay between AMX administration and AICN onset was 1 (IQR, 1 to 3) day; 30, 4, and 11 patients developed KDIGO stage 1, 2, and 3 acute kidney injury, respectively. Delay between AICN onset and kidney function recovery was 4 (IQR, 2 to 6) days. Precipitating factors were identified in only one-third of cases. Twelve patients required intensive care unit admission, and 8 needed renal replacement therapy. Neither chronic kidney disease nor death was observed. We confirmed the recent and dramatic increase of AICN in the Paris RCPVs since 2010. The absence of precipitating factors in the majority of cases and the onset of AICN in apparent routine indications, such as surgical prophylaxis, are alarming and justify a high vigilance from all AMX prescribers.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; adverse drug reaction; amoxicillin; amoxicillin-induced crystal nephropathy; crystals.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Geddes AM, Gould IM. 2010. Ampicillin, amoxicillin and other ampicillin-like penicillins, p 65–92. In Grayson ML, Crowe SM, McCarthy JS, Mills J, Mouton JW, Norbby SR, Paterson DL, Pfaller MA (ed), Kucers' the use of antibiotics, 6th ed CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources