Polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated gold nanoparticles inhibit endothelial cell viability, proliferation, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation and reduce the magnitude of endothelial-independent dilator responses in isolated aortic vessels
- PMID: 29263670
- PMCID: PMC5732551
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S133093
Polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated gold nanoparticles inhibit endothelial cell viability, proliferation, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation and reduce the magnitude of endothelial-independent dilator responses in isolated aortic vessels
Abstract
Background: Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) demonstrate clinical potential for drug delivery and imaging diagnostics. As AuNPs aggregate in physiological fluids, polymer-surface modifications are utilized to allow their stabilization and enhance their retention time in blood. However, the impact of AuNPs on blood vessel function remains poorly understood. In the present study, we investigated the effects of AuNPs and their stabilizers on endothelial cell (EC) and vasodilator function.
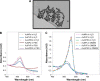
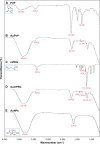
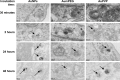
Materials and methods: Citrate-stabilized AuNPs (12±3 nm) were synthesized and surface-modified using mercapto polyethylene glycol (mPEG) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) polymers. Their uptake by isolated ECs and whole vessels was visualized using transmission electron microscopy and quantified using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Their biological effects on EC proliferation, viability, apoptosis, and the ERK1/2-signaling pathway were determined using automated cell counting, flow cytometry, and Western blotting, respectively. Endothelial-dependent and independent vasodilator functions were assessed using isolated murine aortic vessel rings ex vivo.
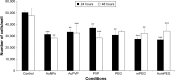
Results: AuNPs were located in endothelial endosomes within 30 minutes' exposure, while their surface modification delayed this cellular uptake over time. After 24 hours' exposure, all AuNPs (including polymer-modified AuNPs) induced apoptosis and decreased cell viability/proliferation. These inhibitory effects were lost after 48 hours' exposure (except for the PVP-modified AuNPs). Furthermore, all AuNPs decreased acetylcholine (ACh)-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, a key signaling protein of cell function. mPEG-modified AuNPs had lower cytostatic effects than PVP-modified AuNPs. Citrate-stabilized AuNPs did not alter endothelial-dependent vasodilation induced by ACh, but attenuated endothelial-independent responses induced by sodium nitroprusside. PVP-modified AuNPs attenuated ACh-induced dilation, whereas mPEG-modified AuNPs did not, though this was dose-related.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that mPEG-modified AuNPs at a therapeutic dosage showed lower cytostatic effects and were less detrimental to vasodilator function than PVP-modified AuNPs, indicating greater potential as agents for diagnostic imaging and therapy.
Keywords: artery; cell culture; gold; nanoparticles; vascular; vasodilation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uptake and cytotoxicity of citrate-coated gold nanospheres: Comparative studies on human endothelial and epithelial cells.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012 Jul 3;9:23. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-9-23. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22759355 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of polymer-modified gold nanoparticles on brain endothelial cells: exclusion of endoplasmic reticulum stress as a potential risk factor.Nanotoxicology. 2016 Nov;10(9):1341-50. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2016.1214761. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Nanotoxicology. 2016. PMID: 27492761 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity, intracellular localization and exocytosis of citrate capped and PEG functionalized gold nanoparticles in human hepatocyte and kidney cells.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016 Aug;32(4):305-21. doi: 10.1007/s10565-016-9336-y. Epub 2016 May 16. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27184667
-
Current trends in using polymer coated gold nanoparticles for cancer therapy.Int J Pharm. 2015 Apr 30;484(1-2):252-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.02.038. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25701627 Review.
-
Synthesis, Chemical-Physical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications of Functional Gold Nanoparticles: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Sep 26;26(19):5823. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195823. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gold@Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanocomposite Hydrogel Loaded with Estrogen for the Treatment of Skin Photoaging.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 12;20:4571-4587. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S511388. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40242609 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol-Mediated Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxicity of Metal Nanoparticles in Human Keratinocyte Cells.ACS Omega. 2021 Oct 21;6(43):29078-29090. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04303. eCollection 2021 Nov 2. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34746597 Free PMC article.
-
Theranostics Aspects of Various Nanoparticles in Veterinary Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 24;19(11):3299. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113299. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30352960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated Nanocomposite Hydrogel Gelation Times Independent of Gold Nanoparticle Ligand Functionality.ACS Omega. 2024 Oct 14;9(42):42858-42867. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05102. eCollection 2024 Oct 22. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39464430 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Anticancer Activity of Phytomolecules Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Aqueous Extracts of Zingiber officinale (Ginger) and Nigella sativa L. Seeds (Black Cumin).Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 18;14(12):3368. doi: 10.3390/ma14123368. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stern JM, Solomonov VV, Sazykina E, Schwartz JA, Gad SC, Goodrich GP. Initial evaluation of the safety of nanoshell-directed photothermal therapy in the treatment of prostate disease. Int J Toxicol. 2016;35(1):38–46. - PubMed
-
- Nanospectra Biosciences Pilot study of AuroLase therapy in refractory and/or recurrent tumors of the head and neck. [Accessed March 16, 2017]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00848042 NLM identifier: NCT00848042.
-
- Cui W, Li J, Zhang Y, Rong H, Lu W, Jiang L. Effects of aggregation and the surface properties of gold nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and cell growth. Nanomedicine. 2012;8(1):46–53. - PubMed
-
- Alkilany AM, Yaseen AI, Kailani MH. Synthesis of monodispersed gold nanoparticles with exceptional colloidal stability with grafted polyethylene glycol-g-polyvinyl alcohol. J Nanomater. 2015;2015:712359.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

