Recent advances in the management of transient ischemic attacks
- PMID: 29263784
- PMCID: PMC5658709
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.12358.1
Recent advances in the management of transient ischemic attacks
Abstract
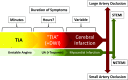
Significant advances in our understanding of transient ischemic attack (TIA) have taken place since it was first recognized as a major risk factor for stroke during the late 1950's. Recently, numerous studies have consistently shown that patients who have experienced a TIA constitute a heterogeneous population, with multiple causative factors as well as an average 5-10% risk of suffering a stroke during the 30 days that follow the index event. These two attributes have driven the most important changes in the management of TIA patients over the last decade, with particular attention paid to effective stroke risk stratification, efficient and comprehensive diagnostic assessment, and a sound therapeutic approach, destined to reduce the risk of subsequent ischemic stroke. This review is an outline of these changes, including a discussion of their advantages and disadvantages, and references to how new trends are likely to influence the future care of these patients.
Keywords: TIA; anticoagulants; antiplatelet therapy; arterial revascularization; stroke risk stratification; transient ischemic attack.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Fisher CM: Intermittent Cerebral Ischemia. In: Wright ISM CH, ed. Cerebral Vascular Disease New York: Grune & Stratton,1958;81–97.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

