Constellation: a tool for rapid, automated phenotype assignment of a highly polymorphic pharmacogene, CYP2D6, from whole-genome sequences
- PMID: 29263805
- PMCID: PMC5685293
- DOI: 10.1038/npjgenmed.2015.7
Constellation: a tool for rapid, automated phenotype assignment of a highly polymorphic pharmacogene, CYP2D6, from whole-genome sequences
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Constellation: a tool for rapid, automated phenotype assignment of a highly polymorphic pharmacogene, CYP2D6, from whole-genome sequences.NPJ Genom Med. 2017 Jan 11;2:16039. doi: 10.1038/npjgenmed.2016.39. eCollection 2017. NPJ Genom Med. 2017. PMID: 29266105 Free PMC article.
Abstract
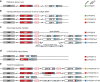
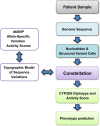
An important component of precision medicine-the use of whole-genome sequencing (WGS) to guide lifelong healthcare-is electronic decision support to inform drug choice and dosing. To achieve this, automated identification of genetic variation in genes involved in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and response (ADMER) is required. CYP2D6 is a major enzyme for drug bioactivation and elimination. CYP2D6 activity is predominantly governed by genetic variation; however, it is technically arduous to haplotype. Not only is the nucleotide sequence of CYP2D6 highly polymorphic, but the locus also features diverse structural variations, including gene deletion, duplication, multiplication events and rearrangements with the nonfunctional, neighbouring CYP2D7 and CYP2D8 genes. We developed Constellation, a probabilistic scoring system, enabling automated ascertainment of CYP2D6 activity scores from 2×100 paired-end WGS. The consensus reference method included TaqMan genotyping assays, quantitative copy-number variation determination and Sanger sequencing. When compared with the consensus reference Constellation had an analytic sensitivity of 97% (59 of 61 diplotypes) and analytic specificity of 95% (116 of 122 haplotypes). All extreme phenotypes, i.e., poor and ultrarapid metabolisers were accurately identified by Constellation. Constellation is anticipated to be extensible to functional variation in all ADMER genes, and to be performed at marginal incremental financial and computational costs in the setting of diagnostic WGS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou, S. F. Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part I. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 48, 689–723 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Zhou, S. F. Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: part II. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 48, 761–804 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Sim, S. C. & Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Update on Allele Nomenclature for Human Cytochromes P450 and the Human Cytochrome P450 Allele (CYP-Allele) Nomenclature Database. Methods Mol. Biol. 987, 251–259 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Koren, G. , Cairns, J. , Chitayat, D. , Gaedigk, A. & Leeder, S. J. Pharmacogenetics of morphine poisoning in a breastfed neonate of a codeine-prescribed mother. Lancet 368, 704 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Prows, C. A. et al. Codeine-related adverse drug reactions in children following tonsillectomy: a prospective study. Laryngoscope 124, 1242–1250 (2014). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

