Antibody therapies for the prevention and treatment of viral infections
- PMID: 29263875
- PMCID: PMC5627241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-017-0019-3
Antibody therapies for the prevention and treatment of viral infections
Abstract
Antibodies are an important component in host immune responses to viral pathogens. Because of their unique maturation process, antibodies can evolve to be highly specific to viral antigens. Physicians and researchers have been relying on such high specificity in their quest to understand host-viral interaction and viral pathogenesis mechanisms and to find potential cures for viral infection and disease. With more than 60 recombinant monoclonal antibodies developed for human use in the last 20 years, monoclonal antibodies are now considered a viable therapeutic modality for infectious disease targets, including newly emerging viral pathogens such as Ebola representing heightened public health concerns, as well as pathogens that have long been known, such as human cytomegalovirus. Here, we summarize some recent advances in identification and characterization of monoclonal antibodies suitable as drug candidates for clinical evaluation, and review some promising candidates in the development pipeline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

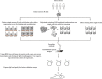
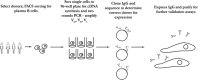
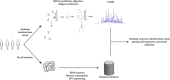
References
-
- Ehrlich, P. Partial cell functions—Nobel lecture, December 11, 1908 in Physiology or Medicine: including Presentation Speeches and Laureates’ Biographies. 304–320 (Elsevier Publisher, 1908).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

