Inhibiting cancer cell hallmark features through nuclear export inhibition
- PMID: 29263896
- PMCID: PMC5661660
- DOI: 10.1038/sigtrans.2016.10
Inhibiting cancer cell hallmark features through nuclear export inhibition
Abstract
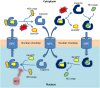
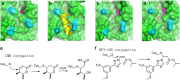
Treating cancer through inhibition of nuclear export is one of the best examples of basic research translation into clinical application. Nuclear export factor chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1; Xpo1 and exportin-1) controls cellular localization and function of numerous proteins that are critical for the development of many cancer hallmarks. The diverse actions of CRM1 are likely to explain the broad ranging anti-cancer potency of CRM1 inhibitors observed in pre-clinical studies and/or clinical trials (phase I-III) on both advanced-stage solid and hematological tumors. In this review, we compare and contrast the mechanisms of action of different CRM1 inhibitors, and discuss the potential benefit of unexplored non-covalent CRM1 inhibitors. This emerging field has uncovered that nuclear export inhibition is well poised as an attractive target towards low-toxicity broad-spectrum potent anti-cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of the nuclear export protein chromosomal region maintenance/exportin 1/Xpo1 is a prognostic factor in human ovarian cancer.Cancer. 2008 Apr 15;112(8):1733-43. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23354. Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18306389
-
Novel-and Not So Novel-Inhibitors of the Multifunctional CRM1 Protein.Oncol Rev. 2024 Aug 5;18:1427497. doi: 10.3389/or.2024.1427497. eCollection 2024. Oncol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39161560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical translation of nuclear export inhibitors in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Aug;27:74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24755012 Review.
-
The past, present, and future of CRM1/XPO1 inhibitors.Stem Cell Investig. 2019 Feb 25;6:6. doi: 10.21037/sci.2019.02.03. eCollection 2019. Stem Cell Investig. 2019. PMID: 30976603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of CRM1.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 7;11:625. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00625. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32574233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear transport proteins: structure, function, and disease relevance.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 10;8(1):425. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01649-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37945593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of exportin retention in the cell nucleus.J Cell Biol. 2024 Feb 5;223(2):e202306094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202306094. Epub 2024 Jan 19. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38241019 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 Screening of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Transformed Cells Identifies XPO1 as a Vulnerable Target of Cancer Cells.mBio. 2019 May 14;10(3):e00866-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00866-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31088931 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Translation of mRNA as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019 Aug;14(4):219-227. doi: 10.1007/s11899-019-00530-y. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019. PMID: 31231778 Review.
-
Case report: Light-chain amyloidosis responsive to selinexor in combination with daratumumab and dexamethasone (SDd) therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 May 2;11:1363805. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1363805. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38756941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

