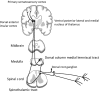
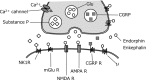
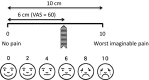
Management of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 29263992
- PMCID: PMC5689392
- DOI: 10.1002/jgf2.5
Management of neuropathic pain
Abstract
Neuropathic pain is intractable pain caused by damage to the nervous system. Recent approval and expansion of the indications of a series of drugs are expected to improve the treatment strategies for neuropathic pain. Here, we present an outline of pain transmission pathways and relevant pharmacological effects, along with points to consider in the use of neuropathic pain medications according to the guidelines of Japan Society of Pain Clinicians. The content of this article is almost similar to my other Japanese article that was published in the Journal of the Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. Although complete recovery from pain may be difficult, pharmacotherapy can relieve pain, thereby improving the patients' quality of life.
Keywords: duloxetine; neuropathic pain; pregabalin; tramadol; tricyclic antidepressants.
Figures
References
-
- Nishikawa N. Treatment of neuropathic pain. J Jpn Soc Int Med. 2013;102:2001–8. - PubMed
-
- Loesera JD, Treedeb RD. The Kyoto protocol of IASP Basic Pain Terminology. Pain. 2008;137:473–7. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D, Lantéri‐Minet M, Attal N, et al. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008;136:380–7. - PubMed
-
- Miaskowski C, Nurmikko TJ, Portenoy RK, et al. Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence‐based recommendations. Pain. 2007;132:237–51. - PubMed
-
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Haanpää M, et al. EFNS guidelines on pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13:1153–69. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources