Serum Testosterone Concentrations Remain Stable Between Injections in Patients Receiving Subcutaneous Testosterone
- PMID: 29264562
- PMCID: PMC5686655
- DOI: 10.1210/js.2017-00148
Serum Testosterone Concentrations Remain Stable Between Injections in Patients Receiving Subcutaneous Testosterone
Abstract
Purpose: Intramuscular (IM) testosterone is the most common modality for testosterone therapy of both male hypogonadism and female-to-male (FTM) gender transition. However, IM injections can be painful and often are not self-administered by the patient. The objective of this study was to further characterize subcutaneous (SC) administration of testosterone as an effective and safe alternative to IM injections by evaluating the pharmacodynamics of serum total and free testosterone concentrations between weekly testosterone injections.
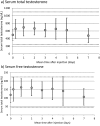
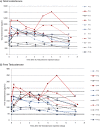
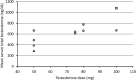
Methods: Eleven FTM transgender patients already receiving weekly SC testosterone cypionate with documented therapeutic levels prior to enrollment had free and total serum testosterone levels measured at eight different time points during a 1-week dosing interval.
Results: Mean levels of total and free testosterone were stable and remained well within the normal range between injections. Overall mean ± standard deviation levels for the seven samples taken between injections were 627 ± 206 ng/dL (range, 205 to 1410) for total testosterone and 146 ± 51 pg/mL (range, 38 to 348) for free testosterone. No adverse effects were encountered.
Conclusions: The results of this study support use of SC testosterone to achieve therapeutic and stable serum testosterone levels for the purpose of gender transition. It is anticipated that these results can be extended to hypogonadal men. This route may be preferred over IM testosterone because it is relatively painless and easy to self-inject thus allowing for the convenience and economy of patient self-administration.
Keywords: pharmacokinetics; subcutaneous testosterone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Testosterone Therapy With Subcutaneous Injections: A Safe, Practical, and Reasonable Option.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Feb 17;107(3):614-626. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab772. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34698352 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous Injection of Testosterone Is an Effective and Preferred Alternative to Intramuscular Injection: Demonstration in Female-to-Male Transgender Patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jul 1;102(7):2349-2355. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00359. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28379417
-
Pharmacokinetics and safety of long-acting testosterone undecanoate injections in hypogonadal men: an 84-week phase III clinical trial.J Androl. 2010 Sep-Oct;31(5):457-65. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.009597. Epub 2010 Feb 4. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 20133964 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Acceptability of Subcutaneous Injection of Testosterone Undecanoate.J Endocr Soc. 2019 Jun 28;3(8):1531-1540. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00134. eCollection 2019 Aug 1. J Endocr Soc. 2019. PMID: 31384715 Free PMC article.
-
Testosterone therapy--what, when and to whom?Aging Male. 2004 Dec;7(4):319-24. doi: 10.1080/13685530400016557. Aging Male. 2004. PMID: 15799128 Review.
Cited by
-
Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Hypogonadal Men.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2022 Mar;51(1):77-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2021.11.005. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 35216722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcutaneous Testosterone Is Effective and Safe as Gender-Affirming Hormone Therapy in Transmasculine and Gender-Diverse Adolescents and Young Adults: A Single Center's 8-Year Experience.Transgend Health. 2021 Dec 2;6(6):343-352. doi: 10.1089/trgh.2020.0103. eCollection 2021 Dec. Transgend Health. 2021. PMID: 34988290 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen Inhibition of Reproductive Neuroendocrine Function in Females and Transgender Males.Endocrinology. 2024 Aug 27;165(10):bqae113. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae113. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39207217 Review.
-
Medical transition for gender diverse patients.Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2020 Dec;9(4):166-177. doi: 10.1007/s13669-020-00297-7. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2020. PMID: 36714061 Free PMC article.
-
Testosterone Therapy With Subcutaneous Injections: A Safe, Practical, and Reasonable Option.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Feb 17;107(3):614-626. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab772. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34698352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, Matsumoto AM, Snyder PJ, Swerdloff RS, Montori VM; Task Force, Endocrine Society . Testosterone therapy in men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(6):2536–2559. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PJ, Lawrence DA. Treatment of male hypogonadism with testosterone enanthate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980;51(6):1335–1339. - PubMed
-
- Sokol RZ, Palacios A, Campfield LA, Saul C, Swerdloff RS. Comparison of the kinetics of injectable testosterone in eugonadal and hypogonadal men. Fertil Steril. 1982;37(3):425–430. - PubMed
-
- Gooren LJ, Bunck MC. Androgen replacement therapy: present and future. Drugs. 2004;64(17):1861–1891. - PubMed
-
- Nieschlag E. Testosterone treatment comes of age: new options for hypogonadal men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006;65(3):275–281. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
