Siglec-1 inhibits RSV-induced interferon gamma production by adult T cells in contrast to newborn T cells
- PMID: 29266251
- PMCID: PMC5947594
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201747161
Siglec-1 inhibits RSV-induced interferon gamma production by adult T cells in contrast to newborn T cells
Abstract
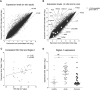
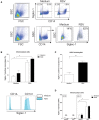
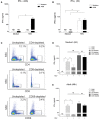
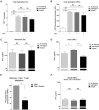
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) plays an important role in the antiviral immune response during respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. Monocytes and T cells are recruited to the site of RSV infection, but it is unclear whether cell-cell interactions between monocytes and T cells regulate IFN-γ production. In this study, micro-array data identified the upregulation of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin 1 (Siglec-1) in human RSV-infected infants. In vitro, RSV increased expression of Siglec-1 on healthy newborn and adult monocytes. RSV-induced Siglec-1 on monocytes inhibited IFN-γ production by adult CD4+ T cells. In contrast, IFN-γ production by RSV in newborns was not affected by Siglec-1. The ligand for Siglec-1, CD43, is highly expressed on adult CD4+ T cells compared to newborns. Our data show that Siglec-1 reduces IFN-γ release by adult T cells possibly by binding to the highly expressed CD43. The Siglec-1-dependent inhibition of IFN-γ in adults and the low expression of CD43 on newborn T cells provides a better understanding of the immune response against RSV in early life and adulthood.
Keywords: CD43; Interferon gamma; Newborns; Respiratory syncytial virus; Siglec-1.
© 2017 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Henderson, F. W. , Collier, A. M. , Clyde, W. A., Jr. and Denny, F. W. , Respiratory‐syncytial‐virus infections, reinfections and immunity. A prospective, longitudinal study in young children. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979. 300: 530–534. - PubMed
-
- Han, L. L. , Alexander, J. P. and Anderson, L. J. , Respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia among the elderly: an assessment of disease burden. J. Infect. Dis. 1999. 179: 25–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

