Ertugliflozin plus sitagliptin versus either individual agent over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin: The VERTIS FACTORIAL randomized trial
- PMID: 29266675
- PMCID: PMC5947297
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13194
Ertugliflozin plus sitagliptin versus either individual agent over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin: The VERTIS FACTORIAL randomized trial
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin and sitagliptin co-administration vs the individual agents in patients with type 2 diabetes who are inadequately controlled with metformin.
Methods: In this study (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT02099110), patients with glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥7.5% and ≤11.0% (≥58 and ≤97 mmol/mol) with metformin ≥1500 mg/d (n = 1233) were randomized to ertugliflozin 5 (E5) or 15 (E15) mg/d, sitagliptin 100 mg/d (S100) or to co-administration of E5/S100 or E15/S100. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in HbA1c at Week 26.
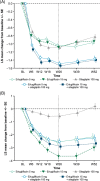
Results: At Week 26, least squares mean HbA1c reductions from baseline were greater with E5/S100 (-1.5%) and E15/S100 (-1.5%) than with individual agents (-1.0%, -1.1% and -1.1% for E5, E15 and S100, respectively; P < .001 for all comparisons). HbA1c <7.0% (<53 mmol/mol) was achieved by 26.4%, 31.9%, 32.8%, 52.3% and 49.2% of patients in the E5, E15, S100, E5/S100 and E15/S100 groups, respectively. Fasting plasma glucose reductions were significantly greater with E5/S100 and E15/S100 compared with individual agents. Body weight and systolic blood pressure (SBP) significantly decreased with E5/S100 and E15/S100 vs S100 alone. Glycaemic control, body weight and SBP effects of ertugliflozin were maintained to Week 52. Genital mycotic infections were more common among ertugliflozin-treated patients compared with those treated with S100. Incidences of symptomatic hypoglycaemia and adverse events related to hypovolaemia or urinary tract infection were similar among groups.
Conclusions: In patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes while using metformin, co-administration of ertugliflozin and sitagliptin provided more effective glycaemic control through 52 weeks compared with the individual agents.
Keywords: DPP-IV inhibitor; SGLT2 inhibitor; clinical trial; glycaemic control; phase III study; type 2 diabetes.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
R. E. P. is a consultant (fees paid to institution) for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ligand Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Lilly, Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, Novo Nordisk Inc. and Takeda; has received research support from Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, Sanofi‐Aventis US, LLC, Takeda, Lilly and Novo Nordisk Inc.; is on speaker's bureaus (fees paid to institution) for AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk Inc.; and reports other funding from Novo Nordisk Inc. A. R., G. G., S. B. H., S. S., J. J, S. S. E. and B. L. are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, and may own stock and/or hold stock options in the company. R. E. was an employee of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey at the time the study was conducted. Y. Q. is an employee of MSD R & D (China) Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey and may own stock and/or hold stock options in the company. S. G. T. and J. P. M. are employees and shareholders of Pfizer Inc.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . 8. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:S64‐S74. - PubMed
-
- Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetic characteristics and clinical efficacy of an SGLT2 inhibitor plus DPP‐4 inhibitor combination therapy in type 2 diabetes. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56:703‐718. - PubMed
-
- Kalgutkar AS, Tugnait M, Zhu T, et al. Preclinical species and human disposition of PF‐04971729, a selective inhibitor of the sodium‐dependent glucose cotransporter 2 and clinical candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39:1609‐1619. - PubMed
-
- Amin NB, Wang X, Jain SM, Lee DS, Nucci G, Rusnak JM. Dose‐ranging efficacy and safety study of ertugliflozin, a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes on a background of metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:591‐598. - PubMed
-
- Terra SG, Focht K, Davies M, et al. Phase III, efficacy and safety study of ertugliflozin monotherapy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise alone. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:721‐728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical