Not like breast cancer, but like breast cancer: micrometastasis and micropapillary structure in lung cancer
- PMID: 29268462
- PMCID: PMC5721054
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.09.105
Not like breast cancer, but like breast cancer: micrometastasis and micropapillary structure in lung cancer
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
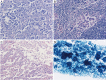
Comment on
-
Relationship of Lymph Node Micrometastasis and Micropapillary Component and Their Joint Influence on Prognosis of Patients With Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2017 Sep;41(9):1212-1220. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000901. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28692600
Similar articles
-
Relationship of Lymph Node Micrometastasis and Micropapillary Component and Their Joint Influence on Prognosis of Patients With Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2017 Sep;41(9):1212-1220. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000901. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28692600
-
Relationship between micropapillary component and micrometastasis in the regional lymph nodes of patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma.Histopathology. 2004 Dec;45(6):580-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2004.01953.x. Histopathology. 2004. PMID: 15569048
-
Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast metastatic to the urinary bladder and endometrium: diagnostic pitfalls and review of the literature of tumors with micropapillary features.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2003 Apr;7(2):112-9. doi: 10.1053/adpa.2003.50015. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12715337
-
[Research Progress of Lymph Node Micrometastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Jul 20;21(7):547-552. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.07.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30037376 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer.Br J Surg. 2003 Mar;90(3):290-301. doi: 10.1002/bjs.4107. Br J Surg. 2003. PMID: 12594663 Review.
Cited by
-
Perioperative Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Era of Immunotherapy.Cells. 2025 Jun 25;14(13):971. doi: 10.3390/cells14130971. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643492 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siriaunkgul S, Tavassoli FA. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Mod Pathol 1993;6:660-2. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Ohta Y, Minato H, et al. Nodal occult metastasis in patients with peripheral lung adenocarcinoma of 2.0 cm or less in diameter. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;71:1772-7; discussion 1777-8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
