Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma-a multicenter analysis of the German working group "Stereotactic Radiotherapy"
- PMID: 29268521
- PMCID: PMC5721071
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.10.108
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma-a multicenter analysis of the German working group "Stereotactic Radiotherapy"
Abstract
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is traditionally considered to be radioresistant. Radiotherapy response rates are believed to improve with hypofractionated, high dose stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). However, limited data exist regarding the role of SBRT in the treatment of pulmonary metastases.
Methods: The working group "Stereotactic Radiotherapy" of the German Society of Radiation Oncology analyzed its multi-institutional database of more than 700 patients who received SBRT for pulmonary metastases. Treatment was performed at 10 centers between 2001 and 2016. Patients with metastatic RCC were included in the study. Tumor characteristics, treatment details, and follow-up data including survival, local control (LC), distant metastases, and toxicity were evaluated.
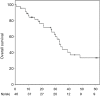
Results: A total of 46 RCC patients treated with SBRT for 67 lung metastases were identified, who received a median total biologically effective dose (BEDiso) at planning target volume (PTV) isocenter of 117.0 Gy (range, 48.0-189.0 Gy). A median fractional dose of 20.8 Gy at isocenter (range, 6.0-37.9 Gy) was administered in a median number of 3 fractions (1-8 fractions). After a median follow-up time of 28.3 months for all patients, 1- and 3-year LC rates were 98.1% and 91.9%, with corresponding 1- and 3-year overall survival (OS) of 84.3% and 43.8%, respectively. Pulmonary metastases treated with BEDiso ≥130 Gy showed a trend for superior LC (P=0.054). OS was significantly improved in both uni- and multivariate analysis for patients with higher Karnofsky performance scale, lower maximum pulmonary metastasis diameter and lack of post-SBRT systemic therapy due to progression (P=0.014; P=0.049; P=0.006). Only mild acute and late toxicity was reported.
Conclusions: SBRT for pulmonary metastases from RCC was associated with low treatment-associated toxicity, promising survival, and excellent LC, especially in those patients receiving a BEDiso ≥130 Gy.
Keywords: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC); extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy; lung metastases; radioresistance; stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Programm. SEER stat fact sheets: kidney and renal pelvic cancer. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute, 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
