Viral Macrodomains: Unique Mediators of Viral Replication and Pathogenesis
- PMID: 29268982
- PMCID: PMC6003825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.11.011
Viral Macrodomains: Unique Mediators of Viral Replication and Pathogenesis
Abstract
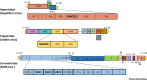
Viruses from the Coronaviridae, Togaviridae, and Hepeviridae families all contain genes that encode a conserved protein domain, called a macrodomain; however, the role of this domain during infection has remained enigmatic. The recent discovery that mammalian macrodomain proteins enzymatically remove ADP-ribose, a common post-translation modification, from proteins has led to an outburst of studies describing both the enzymatic activity and function of viral macrodomains. These new studies have defined these domains as de-ADP-ribosylating enzymes, which indicates that these viruses have evolved to counteract antiviral ADP-ribosylation, likely mediated by poly-ADP-ribose polymerases (PARPs). Here, we comprehensively review this rapidly expanding field, describing the structures and enzymatic activities of viral macrodomains, and discussing their roles in viral replication and pathogenesis.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation; Coronaviridae; Hepeviridae; Togaviridae; interferon (IFN); macrodomain; pathogenesis; poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP); replication.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chambon P. Nicotinamide mononucleotide activation of new DNA-dependent polyadenylic acid synthesizing nuclear enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1963;11:39–43. - PubMed
-
- Holbourn K.P. A family of killer toxins. Exploring the mechanism of ADP-ribosylating toxins. FEBS J. 2006;273:4579–4593. - PubMed
-
- Hottiger M.O. Toward a unified nomenclature for mammalian ADP-ribosyltransferases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010;35:208–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

