Temporal and SUMO-specific SUMOylation contribute to the dynamics of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and spindle integrity during mouse oocyte meiosis
- PMID: 29269218
- PMCID: PMC5805567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.12.011
Temporal and SUMO-specific SUMOylation contribute to the dynamics of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and spindle integrity during mouse oocyte meiosis
Abstract
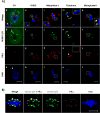
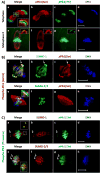
During mammalian meiosis, Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is essential during cell cycle progression. In oocyte maturation, PLK1 expression is well characterized but timing of posttranslational modifications regulating its activity and subcellular localization are less clear. Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) posttranslational modifier proteins have been detected in mammalian gametes but their precise function during gametogenesis is largely unknown. In the present paper we report for mouse oocytes that both PLK1 and phosphorylated PLK1 undergo SUMOylation in meiosis II (MII) oocytes using immunocytochemistry, immunoprecipitation and in vitro SUMOylation assays. At MII, PLK1 is phosphorylated at threonine-210 and serine-137. MII oocyte PLK1 and phosphorylated PLK1 undergo SUMOylation by SUMO-1, -2 and -3 as shown by individual in vitro assays. Using these assays, forms of phosphorylated PLK1 normalized to PLK1 increased significantly and correlated with SUMOylated PLK1 levels. During meiotic progression and maturation, SUMO-1-SUMOylation of PLK1 is involved in spindle formation whereas SUMO-2/3-SUMOylation may regulate PLK1 activity at kinetochore-spindle attachment sites. Microtubule integrity is required for PLK1 localization with SUMO-1 but not with SUMO-2/3. Inhibition of SUMOylation disrupts proper meiotic bipolar spindle organization and spindle-kinetochore attachment. The data show that both temporal and SUMO-specific-SUMOylation play important roles in orchestrating functional dynamics of PLK1 during mouse oocyte meiosis, including subcellular compartmentalization.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Centrosome; Kinetochore; MTOC; Meiosis; SUMOylation; Spindle.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Age-related SUMOylation of PLK1 is essential to meiosis progression in mouse oocytes.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Dec;237(12):4580-4590. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30910. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36317691
-
SUMO-1 plays crucial roles for spindle organization, chromosome congression, and chromosome segregation during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation.Mol Reprod Dev. 2014 Aug;81(8):712-24. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22339. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Mol Reprod Dev. 2014. PMID: 25123474
-
Unique subcellular distribution of phosphorylated Plk1 (Ser137 and Thr210) in mouse oocytes during meiotic division and pPlk1(Ser137) involvement in spindle formation and REC8 cleavage.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(22):3566-79. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1100770. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26654596 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis.Cells. 2023 Jan 2;12(1):187. doi: 10.3390/cells12010187. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36611980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meeting the meiotic challenge: Specializations in mammalian oocyte spindle formation.Mol Reprod Dev. 2018 Mar;85(3):178-187. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22967. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Mol Reprod Dev. 2018. PMID: 29411912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinase PLK1 regulates the disassembly of the lateral elements and the assembly of the inner centromere during the diakinesis/metaphase I transition in male mouse meiosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 13;10:1069946. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1069946. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36733339 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation regulates germinal vesicle breakdown and the Akt/PKB pathway during mouse oocyte maturation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Jul 1;315(1):C115-C121. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00038.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29669220 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Translational Modifications in Oocyte Maturation and Embryo Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 2;9:645318. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645318. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Oocyte Maturation and Related Epigenetic Regulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:654028. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.654028. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33842483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Does SUMO Participate in Spindle Organization?Cells. 2019 Jul 31;8(8):801. doi: 10.3390/cells8080801. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31370271 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrieu A, Brassac T, Galas S, Fisher D, Labbé JC, Dorée M. The Polo-like kinase Plx1 is a component of the MPF amplification loop at the G2/M-phase transition of the cell cycle in Xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1998:1751–7. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud L, Pines J, Nigg EA. GFP tagging reveals human Polo-like kinase 1 at the kinetochore/centromere region of mitotic chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1998;107:424–9. - PubMed
-
- Ban R, Nishida T, Urano T. Mitotic kinase Aurora-B is regulated by SUMO-2/3 conjugation/deconjugation during mitosis. Genes to Cells. 2011;16:652–669. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:1006–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

