CRTC1 mediates preferential transcription at neuronal activity-regulated CRE/TATA promoters
- PMID: 29269871
- PMCID: PMC5740062
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-18215-y
CRTC1 mediates preferential transcription at neuronal activity-regulated CRE/TATA promoters
Abstract
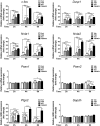
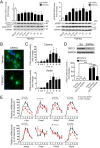
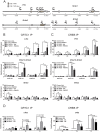
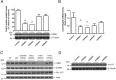
Gene expression mediated by the transcription factor cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) is essential for a wide range of brain processes. The transcriptional coactivartor CREB-regulated transcription coactivator-1 (CRTC1) is required for efficient induction of CREB target genes during neuronal activity. However, the mechanisms regulating induction of specific CREB/CRTC1-dependent genes during neuronal activity remain largely unclear. Here, we investigated the molecular mechanisms regulating activity-dependent gene transcription upon activation of the CREB/CRTC1 signaling pathway in neurons. Depolarization and cAMP signals induce preferential transcription of activity-dependent genes containing promoters with proximal CRE/TATA sequences, such as c-fos, Dusp1, Nr4a1, Nr4a2 and Ptgs2, but not genes with proximal CRE/TATA-less promoters (e.g. Nr4a3, Presenilin-1 and Presenilin-2). Notably, biochemical and chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses reveal constitutive binding of CREB to target gene promoters in the absence of neuronal activity, whereas recruitment of CRTC1 to proximal CRE/TATA promoters depends on neuronal activity. Neuronal activity induces rapid CRTC1 dephosphorylation, nuclear translocation and binding to endogenous CREB. These results indicate that neuronal activity induces a preferential binding of CRTC1 to the transcriptional complex in CRE/TATA-containing promoters to engage activity-dependent transcription in neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sheng, M., McFadden, G. & Greenberg, M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron4, 571–582, 0896-6273(90)90115-V (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

