Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and kidney diseases
- PMID: 29270002
- PMCID: PMC5729884
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S150825
Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and kidney diseases
Abstract
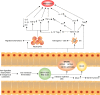
Gut microbiota and its metabolites play pivotal roles in host physiology and pathology. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), as a group of metabolites, exert positive regulatory effects on energy metabolism, hormone secretion, immune inflammation, hypertension, and cancer. The functions of SCFAs are related to their activation of transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors and their inhibition of histone acetylation. Though controversial, growing evidence suggests that SCFAs, which regulate inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, have been involved in kidney disease through the activation of the gut-kidney axis; however, the molecular relationship among gut microbiota-derived metabolites, signaling pathways, and kidney disease remains to be elucidated. This review will provide an overview of the physiology and functions of SCFAs in kidney disease.
Keywords: gut microbiome; gut–kidney axis; kidney diseases; short-chain fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Aguilar-Nascimento JE, Salomao AB, Nochi RJ, Jr, Nascimento M, Neves Jde S. Intraluminal injection of short chain fatty acids diminishes intestinal mucosa injury in experimental ischemia-reperfusion. Acta Cir Bras. 2006;21(1):21–25. - PubMed
-
- Vaziri ND, Zhao YY, Pahl MV. Altered intestinal microbial flora and impaired epithelial barrier structure and function in CKD: the nature, mechanisms, consequences and potential treatment. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2016;31(5):737–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

